[Lesson 2]<< [CONTENTS] >> [Lesson 4]
3.1 The Control Properties
All controls in Visual Basic 2012 IDE have properties. By altering the properties of a control, we are able to customize its appearance and how it responds to an event. Basically, you can set the properties of the controls in the properties window of Visual Basic 2012 IDE at design time or at runtime. Figure 3.1 is the typical properties window for a form. It refers particularly to the interface of the first application you have created in the previous lesson.
In the properties window, the item appears at the top part is the object currently selected (in Figure 3.1, the object selected is Form1). At the bottom part, the items listed in the left column represent the names of various properties associated with the selected object while the items listed in the right column represent the states of the properties. Properties can be set by highlighting the items in the right column then change them by typing or selecting the options available.
You may also alter other properties of a control such as font, location, size, foreground color, background color, MaximizeBox, MinimizeBox and etc. You can also change the properties of the object at runtime to give special effects such as change of color, shape, animation effect and so on.
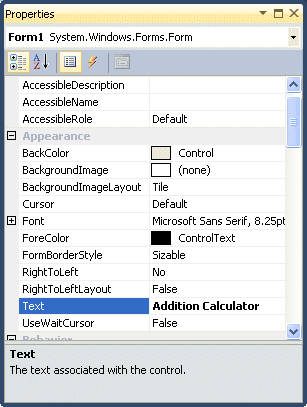
Figure 3.1
Figure 3.2
3.1.1 Customizing the Form
We can customize a form by changing the values in the properties window. First of all, let’s change the title of the form. The title of the form is defined by the Text property and its default name is Form 1. To change the form’s title to any name that you like, simply click in the box on the right of the Text property and type in the new name, in this example, the title is Addition Calculator. After this, you can notice that the form’s title will appear on top of the windows.
In addition, we can customize the form’s color. The following code will change the form color to yellow every time the form is loaded. Visual Basic 2012 uses RGB(Red, Green, Blue) to determine the colors. The RGB code for yellow is 255,255,0 while Me in the code refer to the current form and Backcolor is the property of the form’s background color. The formula to assign the RGB color to the form is Color.FormArbg(RGB code). The event procedure is as follows:
Public Class Form1 Private Sub Form1_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load Me.BackColor = Color.FromArgb(255, 0, 255) End Sub End Class
You may also use the following procedure to assign the color at runtime.
Private Sub Form1_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load Me.BackColor = Color.Magenta End Sub
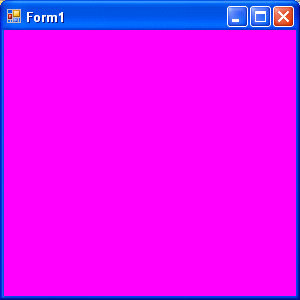
Both procedures above will load the form with a magenta background as follows:
Here are some of the common colors and the corresponding RGB codes. You can always experiment with other combinations, but remember the maximum number for each color is 255 and the minimum number is 0.
The following is another program that allows the user to enter the RGB codes into three different textboxes and when he or she clicks the display color button, the background color of the form will change according to the RGB codes. So, this program allows users to change the color properties of the form at runtime.
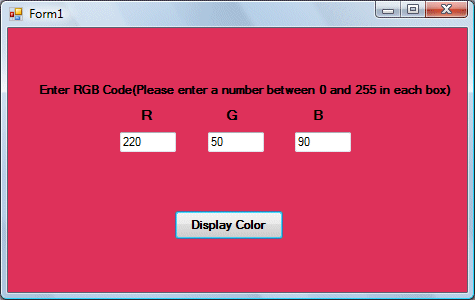
The code
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Dim rgb1, rgb2, rgb3 As Integer rgb1 = TextBox1.Text rgb2 = TextBox2.Text rgb3 = TextBox3.Text Me.BackColor = Color.FromArgb(rgb1, rgb2, rgb3) End Sub
[Lesson 2]<< [CONTENTS] >> [Lesson 4]
*This article has been translated to Serbo-Croatian language by Vera Djuraskovic from Webhostinggeeks.com.

