Lesson 10(b): Formatting Functions
|
|
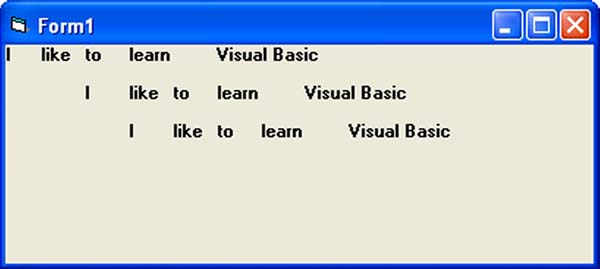
Formatting output is a very important part of programming so that the data can be presented systematically and clearly to the users. Data in Figure 12.3 and Figure 12.4 were presented fairly systematically through the use of commas and some of the functions like Int, Fix and Round. However, to have better control of the output format, we can use a number of formatting functions in Visual basic. The three most common formatting functions in VB are Tab, Space, and Format 10(b)(i) The Tab function Tab (n); x The item x will be displayed at a position that is n spaces from the left border of the output form. There must be a semicolon in between Tab and the items you intend to display (VB will actually do it for you automatically). Example1 .Private Sub Form_Activate Print "I"; Tab(5); "like"; Tab(10); "to"; Tab(15); "learn"; Tab(20); "VB" Print Tab(10); "I"; Tab(15); "like"; Tab(20); "to"; Tab(25); "learn"; Tab(20); "VB" Print Tab(15); "I"; Tab(20); ; "like"; Tab(25); "to"; Tab(30); "learn"; Tab(35); “VB" End sub The Output for example 1 is shown below:
10(b)(ii) The Space function The Space function is very closely linked to the Tab function. However, there is a minor difference. While Tab (n) means the item is placed n spaces from the left border of the screen, the Space function specifies the number of spaces between two consecutive items. For example, the procedure Example 2 Private Sub Form_Activate() Print "Visual"; Space(10); "Basic" End Sub Means that the words Visual and Basic will be separated by 10 spaces
10(b)(iii) The Format function The Format function is a very powerful formatting function which can display the numeric values in various forms. There are two types of Format function, one of them is the built-in or predefined format while another one can be defined by the users. (i) The format of the predefined Format function is Format (n, “style argument”) where n is a number and the list of style arguments is given in the table
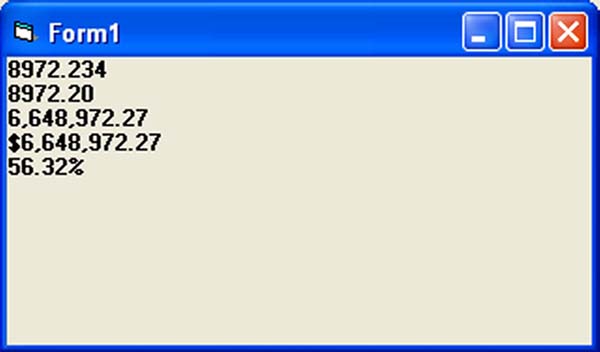
Example 3 Private Sub Form_Activate() Print Format (8972.234, "General Number") Print Format (8972.2, "Fixed") Print Format (6648972.265, "Standard") Print Format (6648972.265, "Currency") Print Format (0.56324, "Percent") End Sub Now, run the program and you will get an output like the figure below:
|