Lesson 24: Errors Handling
Learn to handle runtime errors gracefully in VB2019
Key Takeaway
Proper error handling prevents application crashes and provides users with helpful feedback. VB2019 offers two approaches: traditional On Error and modern Try-Catch.
Error handling is an essential procedure in Visual Basic 2019 programming. Error-free code not only enables the program to run smoothly and efficiently, but it can also prevent all sorts of problems from happening like program crashes or system hangs. Errors often occur due to incorrect input from the user.
Prevent Crashes
Handle unexpected situations gracefully
User Experience
Provide meaningful feedback to users
Debugging Aid
Identify and log issues during development
Robust Code
Create resilient applications that handle edge cases
24.1 Introduction to Error Handling
Errors often occur due to incorrect input from the user. For example, the user might make the mistake of attempting to enter text (string) to a box that is designed to handle only numeric values such as the weight of a person. The computer will not be able to perform arithmetic calculation for text, therefore creating an error. These errors are known as synchronous errors.
Why Handle Errors?
A good programmer should anticipate parts of the program that could trigger errors and write error handling code to help users manage these situations. Writing error handling code is a good practice for Visual Basic 2019 programmers.
Visual Basic 2019 has improved significantly in its built-in error handling capabilities compared to Visual Basic 6. For example, when the user attempts to divide a number by zero, Visual Basic 2019 will not return an error message but gives 'infinity' as the answer.
Common Error Types
| Error Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Invalid Cast | Converting incompatible data types | Converting "ABC" to Integer |
| Divide By Zero | Attempting to divide by zero | 10 / 0 |
| Null Reference | Accessing properties of Nothing | Dim s As String = Nothing s.Length |
| Index Out of Range | Accessing array elements beyond bounds | Dim arr(5) As Integer arr(6) = 10 |
24.2 Using On Error GoTo Syntax
Visual Basic 2019 still supports the VB6 error handling syntax, which is the On Error GoTo program_label structure. The syntax for error handling is:
Where program_label is the section of code designed to handle the error committed by the user. Once an error is detected, the program will jump to the program_label section for error handling.
Example: Handling Division Errors
In this example, we handle errors when users enter non-numeric data into text boxes that should contain numbers. The program_label here is error_handler.
Private Sub BtnCal_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCal.Click ' Hide previous error messages Lbl_ErrMsg.Visible = False Dim firstNum, secondNum As Double ' Set up error handling On Error GoTo error_handler ' Attempt to convert text to numbers firstNum = TxtNum1.Text secondNum = TxtNum2.Text ' Perform calculation Lbl_Answer.Text = firstNum / secondNum ' Exit before error handler if successful Exit Sub error_handler: ' Display error message Lbl_Answer.Text = "Error" Lbl_ErrMsg.Visible = True Lbl_ErrMsg.Text = " One or both of the entries is/are non-numeric! Try again!" End Sub

Figure 24.1: Handling non-numeric input errors
Note on Division by Zero
In Visual Basic 2019, division by zero no longer throws an exception but returns Double.PositiveInfinity, Double.NegativeInfinity, or Double.NaN (Not a Number). This is different from earlier versions of VB.
24.3 Error Handling with Try-Catch
Visual Basic 2019 has a modern approach to error handling using the Try...Catch...End Try structure. This method is more efficient than the old On Error GoTo approach as it can handle various types of errors within a structured block.
[ tryStatements ]
[ Catch [ exception [ As type ] ]
[ catchStatements ]
[ Finally
[ finallyStatements ] ]
End Try
Example: Modern Error Handling
Here's the same division calculator implemented with Try-Catch:
Private Sub BtnCal_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCal.Click Lbl_ErrMsg.Visible = False Dim firstNum, secondNum, answer As Double Try ' Attempt conversion and calculation firstNum = TxtNum1.Text secondNum = TxtNum2.Text answer = firstNum / secondNum Lbl_Answer.Text = answer Catch ex As Exception ' Handle any exceptions Lbl_Answer.Text = "Error" Lbl_ErrMsg.Visible = True Lbl_ErrMsg.Text = " One of the entries is not a number! Try again!" ' Optional: Log the error for debugging ' Debug.WriteLine("Error: " & ex.Message) End Try End Sub
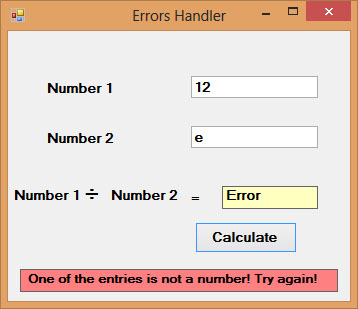
Figure 24.2: Error handling with Try-Catch
Benefits of Try-Catch
- Structured Handling: Errors are contained within specific blocks
- Multiple Exception Types: Catch different exceptions with multiple Catch blocks
- Resource Cleanup: Use Finally block to release resources regardless of errors
- Modern Approach: Aligns with error handling in other .NET languages
- Detailed Information: Exception objects contain detailed error information
Handling Specific Exceptions
You can catch specific types of exceptions to handle different error scenarios appropriately:
Try ' Code that might cause different exceptions Catch ex As InvalidCastException ' Handle invalid type conversions MessageBox.Show("Please enter numeric values only") Catch ex As DivideByZeroException ' Handle division by zero MessageBox.Show("Cannot divide by zero") Catch ex As Exception ' Handle all other exceptions MessageBox.Show("An unexpected error occurred: " & ex.Message) Finally ' Code that always runs (cleanup resources, etc.) ' e.g., connection.Close() End Try
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned how to handle errors in VB2019:
Error Types
Understand common runtime errors like invalid casts and division by zero
Traditional Approach
Implement error handling using On Error GoTo syntax
Modern Approach
Use Try-Catch blocks for structured exception handling
Specific Exceptions
Handle different error types with multiple Catch blocks
Proper error handling is essential for creating robust, user-friendly applications. In the next lesson, we'll explore object-oriented programming in VB2019.
Next Lesson
Learn object-oriented programming concepts in Lesson 25: Object-Oriented Programming.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 2019 Made Easy
Unlock the power of Visual Basic 2019 with this comprehensive, easy-to-follow handbook written by Dr. Liew, renowned educator and founder of the popular programming tutorial website VBtutor.net. Whether you're new to programming or brushing up your skills, this book is your perfect companion to learn Visual Basic 2019 from the ground up.
What You'll Learn:
- Understand Core Programming Concepts: Grasp the foundational principles of Visual Basic 2019, including variables, data types, conditional logic, loops, and event-driven programming.
- Develop Real Windows Desktop Applications: Build fully functional and interactive Windows apps using Visual Studio 2019—guided through step-by-step tutorials.
- Apply Dozens of Ready-to-Use Examples: Explore a rich collection of practical sample programs, from basic calculators to image viewers and database applications.
- Adapt and Reuse Code for Your Own Projects: Customize professionally written code snippets to speed up your development process and bring your ideas to life.
- Package and Deploy Like a Pro: Learn how to compile, test, and distribute your Visual Basic applications seamlessly with built-in deployment tools.

Visual Basic Programming With Code Examples
Visual Basic Programming with Code Examples offers a unique dual-format approach, showcasing sample codes in both Visual Basic 6 (VB6) and VB.NET. This side-by-side presentation helps you understand the evolution of Visual Basic and empowers you to work confidently across both environments.
What You'll Learn:
- Core Concepts Made Easy: Explore data types, control structures, file handling, procedures, user interface design, and more.
- Hands-On Application Building: Design real-world applications, including financial calculators, educational tools, games, multimedia apps, and database systems.
- 48 Practical Code Examples: Study and customize fully explained programs that illustrate key programming techniques.
- Dual-Code Format: Learn to translate and adapt code between VB6 and VB.NET seamlessly.