In this example, we add a few labels, two buttons, and six check boxes. We declare the price of each item using the Const keyword. If a checkbox is being ticked, its state is True else its state is False. To calculate the total amount of purchase, we use the mathematical operator +=. For example, sum+=BN is actually sum=sum+BN. Finally, we use the ToString method to display the amount in currency.
Public Class Form1
Private Sub BtnCal_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCal.Click
Const LX As Integer = 100
Const BN As Integer = 500
Const SD As Integer = 200
Const HD As Integer = 80
Const HM As Integer = 300
Const AM As Integer = 150
Dim sum As Integer
If CheckBox1.Checked = True Then
sum += LX
End If
If CheckBox2.Checked = True Then
sum += BN
End If
If CheckBox3.Checked = True Then
sum += SD
End If
If CheckBox4.Checked = True Then
sum += HD
End If
If CheckBox5.Checked = True Then
sum += HM
End If
If CheckBox6.Checked = True Then
sum += AM
End If
LblTotal.Text = sum.ToString("c")
End Sub
Private Sub BtnReset_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnReset.Click
CheckBox1.Checked = False
CheckBox2.Checked = False
CheckBox3.Checked = False
CheckBox4.Checked = False
CheckBox5.Checked = False
CheckBox6.Checked = False
End Sub
End Class
The Runtime Interface
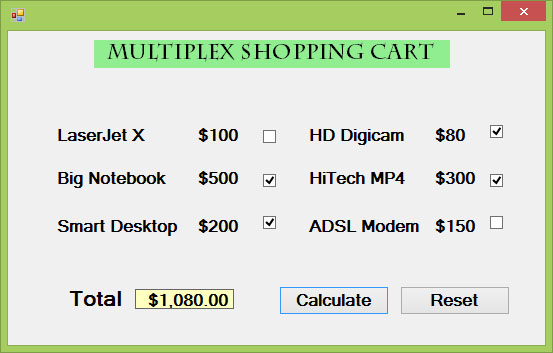
Here is another example
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Const large As Integer = 10.0 Const medium As Integer = 8 Const small As Integer = 5 Dim sum As Integer If CheckBox1.Checked = True Then sum += large End If If CheckBox2.Checked = True Then sum += medium End If If CheckBox3.Checked = True Then sum += small End If Label5.Text = sum.ToString(“c”) End Sub
In this example, the text on the label can be formatting using the three check boxes that represent bold, italic and underline.
Public Class Form1 Private Sub ChkBold_CheckedChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles ChkBold.CheckedChanged If ChkBold.Checked Then LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style Or FontStyle.Bold) Else LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style And Not FontStyle.Bold) End If End Sub Private Sub ChkItalic_CheckedChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles ChkItalic.CheckedChanged If ChkItalic.Checked Then LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style Or FontStyle.Italic) Else LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style And Not FontStyle.Italic) End If End Sub Private Sub ChkUnder_CheckedChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles ChkUnder.CheckedChanged If ChkUnder.Checked Then LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style Or FontStyle.Underline) Else LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style And Not FontStyle.Underline) End If End Sub End Class
* The above program uses the CheckedChanged event to respond to the user selection by checking a particular checkbox, it is similar to the click event. The statement
LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style Or FontStyle.Italic)
will retain the original font type but change it to italic font style.
LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style And Not FontStyle.Italic)
will also retain the original font type but change it to regular font style. (The other statements employ the same logic)
The Output
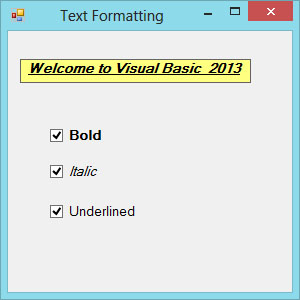
Copyright©2008 Dr.Liew Voon Kiong. All rights reserved |Contact|Privacy Policy