Lesson 35: Connecting to Databases in VB2022
Learn how to establish and manage database connections in your VB2022 applications
Key Takeaway
ADO.NET provides powerful tools for establishing database connections and managing data in VB2022 applications.
Building on the database fundamentals from Lesson 34, we'll now explore how to establish and manage database connections in VB2022. Proper database connectivity is essential for creating applications that can store, retrieve, and manipulate data efficiently.
35.1 Establishing Database Connections
The first step in database programming is establishing a connection to your database. VB2022 uses ADO.NET components for this purpose.
ADO.NET Connection Flow
Database
SqlConnection
SqlDataAdapter
DataTable
UI Controls
Core ADO.NET Components
SqlConnection
Manages the connection to SQL Server
SqlDataAdapter
Bridges data sources and datasets
DataTable
In-memory representation of data
SqlCommand
Executes SQL statements against the database
Example 35.1: Basic Database Connection
This example shows how to establish a connection to SQL Server:
Imports System.Data.SqlClient Public Class DatabaseForm Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load ' Define connection string Dim connString As String = "Server=localhost\SQLEXPRESS;" & _ "Database=ContactsDB;" & _ "Integrated Security=True;" ' Create SqlConnection object Using conn As New SqlConnection(connString) Try ' Open the connection conn.Open() ' Check connection state If conn.State = ConnectionState.Open Then MessageBox.Show("Database connection successful!", "Connection Status", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information) End If Catch ex As SqlException MessageBox.Show("Error connecting to database: " & ex.Message, "Connection Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error) End Try End Using End Sub End Class
35.2 Retrieving and Displaying Data
Once connected, we can retrieve data and display it in our application.
Example 35.2: Retrieving Data with DataAdapter
This example demonstrates how to retrieve data and display it in a DataGridView:
Imports System.Data Imports System.Data.SqlClient Public Class DataForm Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load ' Connection string Dim connString As String = "Server=localhost\SQLEXPRESS;Database=ContactsDB;Integrated Security=True;" ' SQL query Dim query As String = "SELECT ContactID, FirstName, LastName, Email FROM Contacts" ' Create objects Using conn As New SqlConnection(connString) Try conn.Open() ' Create DataAdapter Dim adapter As New SqlDataAdapter(query, conn) ' Create DataTable Dim dt As New DataTable() ' Fill DataTable with data adapter.Fill(dt) ' Bind to DataGridView DataGridView1.DataSource = dt Catch ex As SqlException MessageBox.Show("Database error: " & ex.Message, "Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error) End Try End Using End Sub End Class
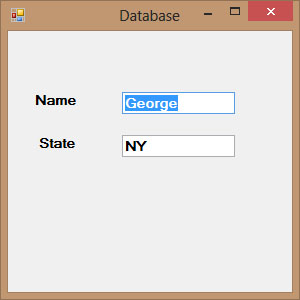
Figure 35.1: Data displayed in a DataGridView
35.3 Navigating Database Records
For applications that need to display one record at a time, we need to implement navigation.
Example 35.3: Record Navigation
This example shows how to navigate through records:
Public Class NavigationForm Private currentPosition As Integer = 0 Private dt As New DataTable Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load ' Load data (implementation similar to previous example) LoadData() ShowCurrentRecord() End Sub Private Sub ShowCurrentRecord() If dt.Rows.Count = 0 Then Return txtName.Text = dt.Rows(currentPosition)("ContactName").ToString() txtState.Text = dt.Rows(currentPosition)("State").ToString() lblPosition.Text = $"Record {currentPosition + 1} of {dt.Rows.Count}" End Sub Private Sub btnFirst_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnFirst.Click currentPosition = 0 ShowCurrentRecord() End Sub Private Sub btnPrevious_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnPrevious.Click If currentPosition > 0 Then currentPosition -= 1 ShowCurrentRecord() End If End Sub Private Sub btnNext_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnNext.Click If currentPosition < dt.Rows.Count - 1 Then currentPosition += 1 ShowCurrentRecord() End If End Sub Private Sub btnLast_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnLast.Click currentPosition = dt.Rows.Count - 1 ShowCurrentRecord() End Sub Private Sub LoadData() ' Define schema dt.Columns.Add("ContactName") dt.Columns.Add("State") ' Add sample data dt.Rows.Add("Alice", "California") dt.Rows.Add("Bob", "Texas") dt.Rows.Add("Charlie", "Florida") End Sub End Class
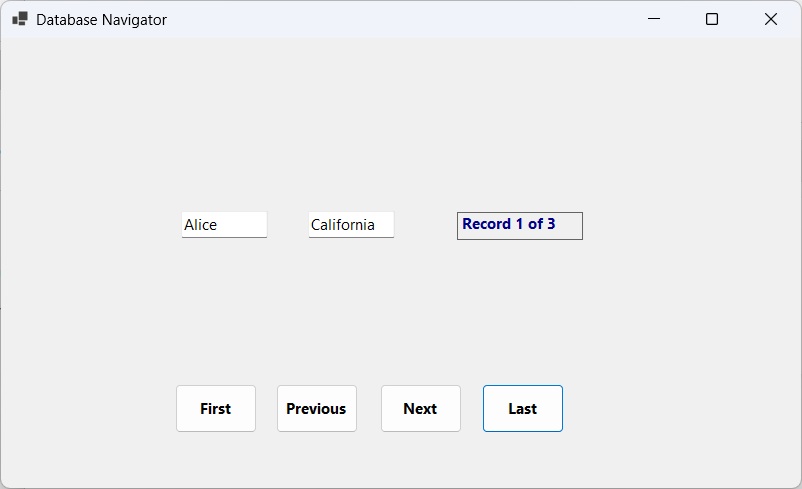
Figure 35.2: Record navigation interface
35.4 Adding New Records
Adding records to a database requires a SqlCommand with parameterized queries.
Example 35.4: Inserting Records
This example shows how to insert a new record into the database:
Imports System.Data.SqlClient Public Class InsertForm Private Sub BtnAdd_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnAdd.Click Dim connString As String = "Server=localhost\SQLEXPRESS;Database=ContactsDB;Integrated Security=True;" Dim query As String = "INSERT INTO Contacts (FirstName, LastName, Email) " & _ "VALUES (@FirstName, @LastName, @Email)" Using conn As New SqlConnection(connString) Using cmd As New SqlCommand(query, conn) ' Add parameters to prevent SQL injection cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@FirstName", txtFirstName.Text) cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@LastName", txtLastName.Text) cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Email", txtEmail.Text) Try conn.Open() Dim rowsAffected = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery() If rowsAffected > 0 Then MessageBox.Show("Record inserted successfully!", "Success", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information) ' Clear form for next entry ClearForm() Else MessageBox.Show("No records were inserted.", "Information", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information) End If Catch ex As SqlException MessageBox.Show("Error inserting record: " & ex.Message, "Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error) End Try End Using End Using End Sub Private Sub ClearForm() txtFirstName.Text = "" txtLastName.Text = "" txtEmail.Text = "" End Sub End Class
Database Connection Summary
Master these essential concepts for database connectivity in VB2022:
| Component | Purpose | Key Method/Property |
|---|---|---|
| SqlConnection | Manages connection to SQL Server | Open(), Close(), ConnectionString |
| SqlDataAdapter | Bridges data source and DataSet/DataTable | Fill(), Update() |
| DataTable | In-memory representation of data | Rows, Columns, NewRow() |
| SqlCommand | Executes SQL commands | ExecuteNonQuery(), Parameters |
Connection Best Practices
Always use the Using statement to ensure connections are properly closed and disposed, even if exceptions occur.
Security First
Always use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection attacks. Never concatenate user input directly into SQL statements.
Error Handling
Properly handle SqlException to provide meaningful error messages and maintain application stability.
Practical Exercises
Apply your database connection knowledge with these hands-on exercises:
Exercise 1: Connection Tester
Create an application that tests database connections with different connection strings and displays success or error messages.
Exercise 2: Product Manager
Build a product management application that retrieves product data from a database and displays it in a DataGridView.
Exercise 3: Record Navigator
Implement a form that displays one record at a time with navigation buttons (First, Previous, Next, Last).
Exercise 4: Data Entry Form
Create a form to add new customer records to the database with validation for required fields.
Exercise 5: Connection Settings
Develop a settings form that allows users to configure and test database connection parameters.
Challenge Exercise: Inventory System
Develop a complete inventory management system with product listing, search, and add new product functionality.
Next Lesson
Learn how to edit and update database records in Lesson 36: Editing Database Data.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 2022 Made Easy
The ultimate beginner-friendly guide for mastering Windows-based application development using Visual Basic in Visual Studio 2022. Whether you're a student, teacher, hobbyist, or self-learner, this book offers a clear, step-by-step approach to help you get started with ease.
What You'll Learn:
- Control structures and procedures
- Decision-making techniques
- Efficient code organization
- Practical application development
- Best practices in VB2022

Mastering Excel VBA 365
Your ultimate step-by-step guide to automating tasks, building macros, and creating powerful applications within Microsoft Excel 365. Whether you're a student, business professional, or aspiring programmer, this comprehensive handbook will help you unlock the full potential of Excel's VBA.
What You'll Learn:
- Control structures in VBA
- Decision-making techniques
- Data processing and analysis
- Report generation
- Automated workflows