Lesson 3: Working with Controls in VB6
Master essential VB6 controls to create interactive applications with professional interfaces
Key Takeaway
VB6 controls are the building blocks of your application's user interface. Understanding how to configure properties and handle events is essential for creating interactive and professional Windows applications.
Welcome to Lesson 3 of our Visual Basic 6 Tutorial! In this lesson, you'll learn how to work with essential VB6 controls to create interactive applications. We'll cover TextBoxes, Labels, CommandButtons, ListBoxes, ComboBoxes, and more, with practical examples you can implement.
3.1 The Control Properties
To create effective event procedures, you need to configure specific properties that dictate a control's appearance and functionality. These properties can be set either through the properties window or dynamically at runtime.
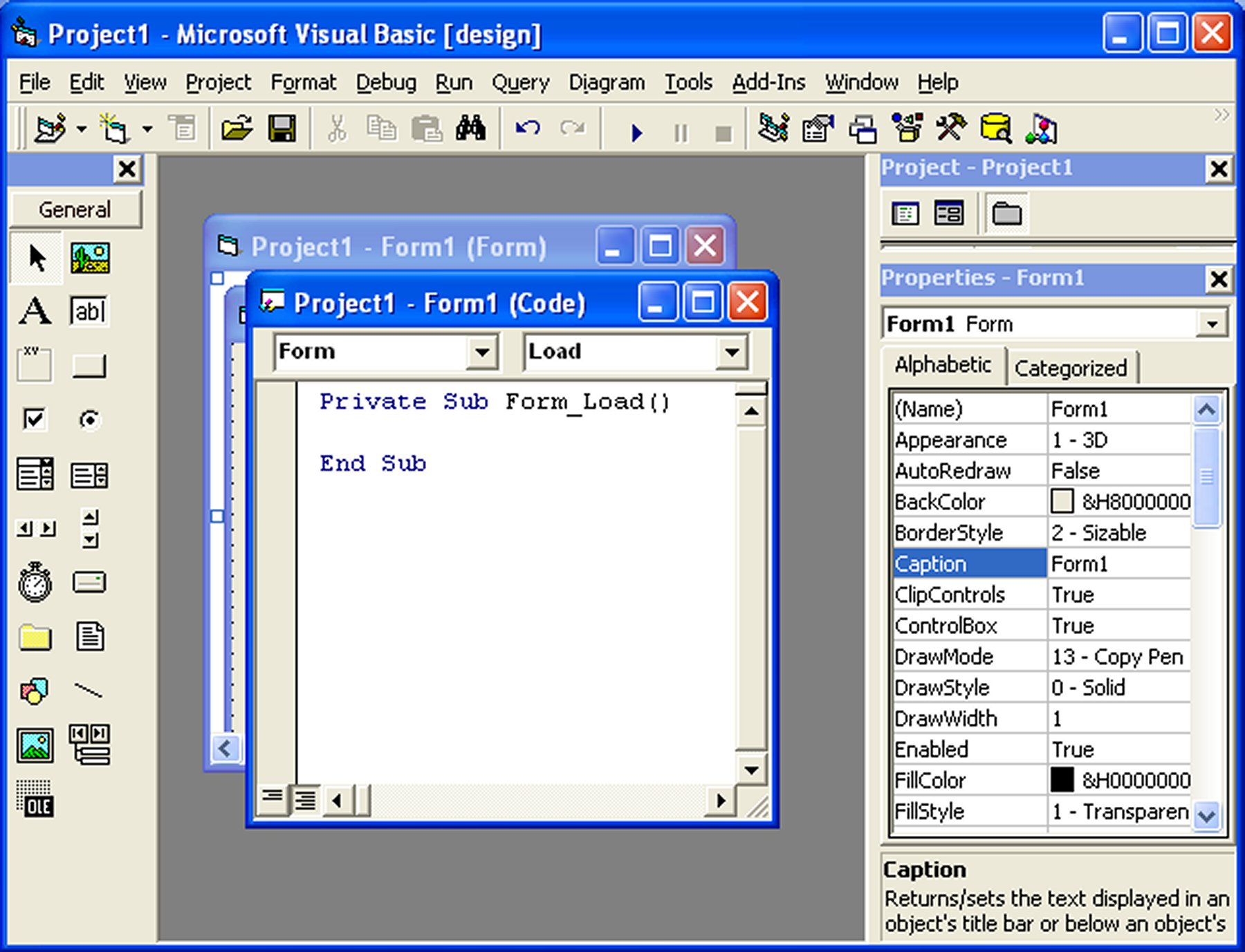
In the properties window, the top section shows the currently selected object. The bottom is divided into columns—the left lists properties, and the right displays their current states. To modify, simply adjust the items in the right column.
1 Changing Properties
Change the form caption by highlighting 'Form1' and entering your text. Customize appearance by selecting 3D/flat style, colors, fonts, and enabling/disabling controls.
2 Runtime Property Changes
You can change properties at runtime to create effects like color changes, animations, and more. VB uses hexadecimal color codes which can be found in properties windows.
Changing Background Color at Runtime
This example changes the background color of the form to red when loaded:
Private Sub Form_Load() Form1.Show Form1.BackColor = &H000000FF& End Sub
Output:
Changing Shape at Runtime
This code changes a shape control to a circle at runtime:
Private Sub Form_Load() Shape1.Shape = 3 End Sub
Important Property Tips
- Set the Caption property clearly so users understand the control's function
- Use meaningful names for the Name property for easier coding and debugging
- Consider when to enable/disable controls using the Enabled property
- Use the Visible property to show/hide controls when appropriate
3.2 Handling Common Controls
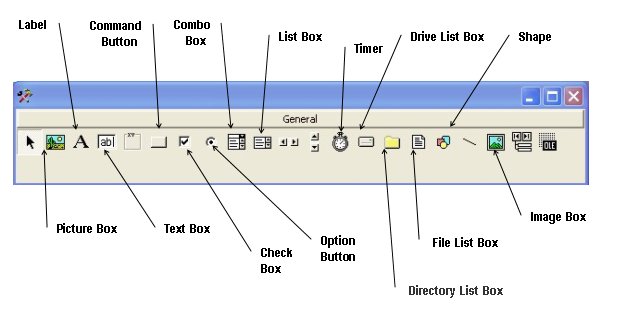
TextBox
Standard control for user input and displaying output. Handles text and numeric data.
Label
Provides instructions and displays output. The Caption property is most important.
CommandButton
Executes procedures triggered by user events, most commonly the Click event.
PictureBox
Handles graphics. Can load pictures at design time or runtime with LoadPicture.
3.2.1 The TextBox Control
The text box accepts input from users and displays output. It handles string and numeric data. Use Val(text) to convert string input to numeric data.
Example: Summation of Two Numbers
This program adds numbers entered in two text boxes and displays the result in a label:
Private Sub Command1_Click() ' Add values from TextBox1 and TextBox2 Dim Sum As Double Sum = Val(Text1.Text) + Val(Text2.Text) ' Display the result in Label1 Label1.Caption = Sum End Sub
Output:

3.2.2 The Label Control
Labels provide instructions and display outputs. The Caption property is essential and can be changed at runtime.
3.2.3 The CommandButton Control
Command buttons execute procedures, typically in response to a Click event:
Private Sub Command1_Click() ' Code to execute when button is clicked ' ... End Sub
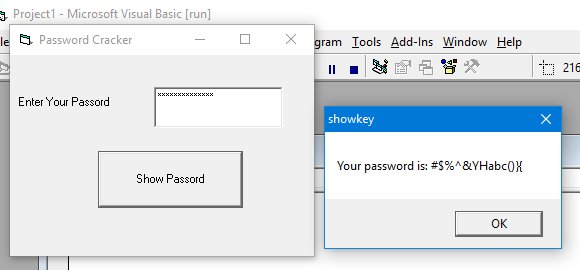
Example: Simple Password Revealer
This program reveals a password entered in a text box with PasswordChar set to '*':
Private Sub cmd_ShowPass_Click() Dim yourpassword As String yourpassword = Txt_Password.Text MsgBox ("Your password is: " & yourpassword) End Sub
Output:
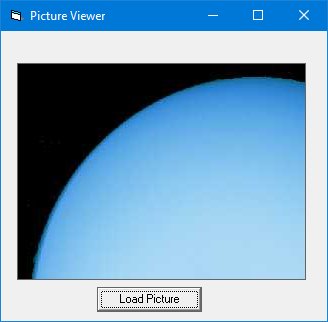
3.2.4 The PictureBox Control
The PictureBox handles graphics. Load images at design time through properties or at runtime with LoadPicture:
Private Sub cmd_LoadPic_Click() Picture1.Picture = LoadPicture("C:\Path\To\Your\Image.jpg") End Sub
3.2.5 The Image Control
Similar to PictureBox but with a key difference - images in an ImageBox are stretchable. Use the same LoadPicture method:
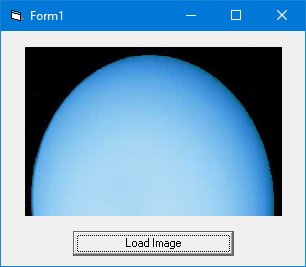
3.2.6 The ListBox Control
Presents a list of items for user selection. Add items with the AddItem method:
Private Sub Form_Load() List1.AddItem "Lesson1" List1.AddItem "Lesson2" List1.AddItem "Lesson3" List1.AddItem "Lesson4" End Sub

3.2.7 The ComboBox Control
Similar to ListBox but presents items in a drop-down list. Add items with AddItem:
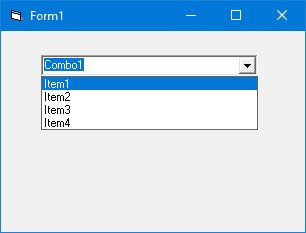
3.2.8 The CheckBox Control
Lets users select or deselect options. Value is 1 when checked and 0 when unchecked:
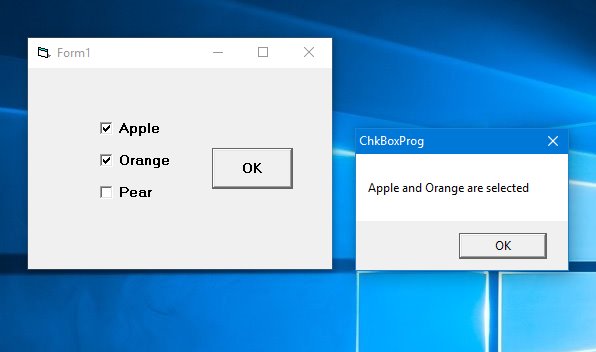
3.2.9 The OptionButton Control
Option buttons work together - when one is selected, others are deselected. Value is True when selected:
Private Sub cmd_SetColor_Click() If Option1.Value = True Then Form1.BackColor = vbRed ElseIf Option2.Value = True Then Form1.BackColor = vbBlue Else Form1.BackColor = vbGreen End If End Sub
3.2.10 The Shape Control
Displays various shapes. Shape property values: 0=rectangle, 1=square, 2=oval, 3=circle, 4=rounded rectangle, 5=rounded square.
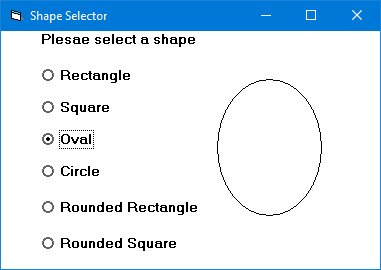
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned how to work with essential VB6 controls:
Control Properties
Configure properties at design time and runtime for visual effects
Input Controls
Mastered TextBox for user input and Label for displaying output
Action Controls
Used CommandButton to execute procedures in response to events
Selection Controls
Implemented ListBox, ComboBox, CheckBox, and OptionButton
You've now built interactive VB6 applications using essential controls and are ready to explore more advanced topics in the next lesson.
Next Lesson
Ready to learn more about VB6 programming? Continue to Lesson 4: Writing the Code.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 6 Made Easy
The ultimate beginner-friendly guide for mastering Windows-based application development using Visual Basic 6. Used as a textbook by universities worldwide.
What You'll Learn:
- Comprehensive coverage of VB6 controls
- Designing professional interfaces
- Event-driven programming techniques
- Practical examples and projects
- Debugging and error handling
- Database integration

Visual Basic 2022 Made Easy
The ultimate guide to VB.NET programming in Visual Studio 2022. Master modern VB development with this comprehensive resource.
What You'll Learn:
- Modern VB.NET control techniques
- Visual Studio 2022 features
- Advanced UI development
- Database programming with ADO.NET
- Web API integration
- Deployment strategies