Lesson 11: Mathematical Operations in VB2019
Master calculations and formulas to build powerful applications
Key Takeaway
Visual Basic 2019 provides powerful arithmetic operators that enable you to perform complex calculations, solve equations, and implement mathematical formulas in your applications.
Mathematical operations are fundamental to programming. In Visual Basic 2019, you can perform calculations using arithmetic operators that closely resemble normal mathematical notation. These operators allow you to build applications that solve equations, perform financial calculations, analyze data, and more.
11.1 Arithmetic Operators
Visual Basic 2019 includes all standard arithmetic operators plus some specialized ones. The operators are very similar to mathematical notation with a few syntax differences:
| Operator | Function | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | 5 + 3 | 8 |
| - | Subtraction | 10 - 4 | 6 |
| * | Multiplication | 6 * 7 | 42 |
| / | Division | 15 / 3 | 5 |
| ^ | Exponentiation | 3 ^ 2 | 9 |
| Mod | Modulus (remainder) | 15 Mod 4 | 3 |
| \ | Integer Division | 19 \ 4 | 4 |
Operator Precedence
Operators follow standard mathematical precedence: Exponentiation (^) is evaluated first, followed by multiplication (*) and division (/), then addition (+) and subtraction (-). Use parentheses to explicitly control the order of operations.
Addition (+)
Used to add two numbers or concatenate strings
Example: result = 5 + 3 ' Returns 8
Exponentiation (^)
Raises a number to the power of another
Example: result = 3 ^ 4 ' Returns 81
Modulus (Mod)
Returns the remainder after division
Example: result = 17 Mod 5 ' Returns 2
11.2 Basic Calculation Examples
Let's explore practical implementations of mathematical operations in VB2019 applications.
11.2.1 Basic Arithmetic Operations
This example demonstrates a simple calculator that performs the four basic arithmetic operations.
Private Sub BtnCalculate_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCalculate.Click ' Get input values Dim num1 As Single = CSng(TxtNum1.Text) Dim num2 As Single = CSng(TxtNum2.Text) ' Perform calculations Dim sum As Single = num1 + num2 Dim diff As Single = num1 - num2 Dim prod As Single = num1 * num2 Dim quot As Single = num1 / num2 ' Display results LblSum.Text = CStr(sum) LblDiff.Text = CStr(diff) LblProduct.Text = CStr(prod) LblQuotient.Text = CStr(quot) End Sub
Output:

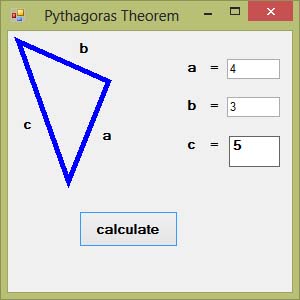
11.2.2 Pythagoras Theorem
This program calculates the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle using Pythagoras Theorem.
Private Sub BtnCalculateHyp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCalculateHyp.Click ' Get side lengths Dim sideA As Double = CDbl(TxtSideA.Text) Dim sideB As Double = CDbl(TxtSideB.Text) ' Calculate hypotenuse using Pythagoras Theorem Dim hypotenuse As Double = Math.Sqrt(sideA ^ 2 + sideB ^ 2) ' Display result LblHypotenuse.Text = "c = " & Math.Round(hypotenuse, 2).ToString() ' Draw a visual representation of the triangle Dim myPen As New Pen(Color.Blue, 3) Dim ptA As New Point(50, 50) Dim ptB As New Point(50 + sideA * 10, 50) Dim ptC As New Point(50, 50 + sideB * 10) Dim points() As Point = {ptA, ptB, ptC} Dim g As Graphics = Me.CreateGraphics() g.Clear(Color.White) g.DrawPolygon(myPen, points) End Sub
Output:
11.3 Practical Applications
Mathematical operations enable you to solve real-world problems. Here are some practical examples:
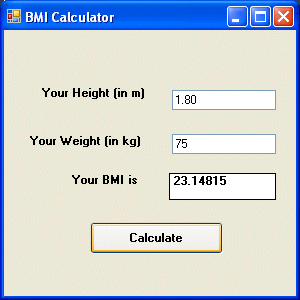
11.3.1 BMI Calculator
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight. It can be calculated using the formula:
Private Sub BtnCalculateBMI_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCalculateBMI.Click ' Get user input Dim height As Double = CDbl(TxtHeight.Text) Dim weight As Double = CDbl(TxtWeight.Text) ' Calculate BMI Dim bmi As Double = weight / (height ^ 2) ' Determine weight status Dim status As String = "" Select Case bmi Case Is < 18.5 status = "Underweight" Case 18.5 To 24.9 status = "Normal weight" Case 25 To 29.9 status = "Overweight" Case Is >= 30 status = "Obesity" End Select ' Display results LblBMI.Text = "BMI: " & Math.Round(bmi, 2).ToString() LblStatus.Text = "Status: " & status End Sub
Output:
11.3.2 Compound Interest Calculator
Compound interest is calculated using the formula:
A = future value
P = principal investment
r = annual interest rate
n = compounds per year
t = years invested
Private Sub BtnCalculateInterest_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCalculateInterest.Click ' Get input values Dim principal As Double = CDbl(TxtPrincipal.Text) Dim rate As Double = CDbl(TxtRate.Text) / 100 ' Convert percentage to decimal Dim years As Integer = CInt(TxtYears.Text) Dim compoundsPerYear As Integer = CInt(TxtCompounds.Text) ' Calculate compound interest Dim amount As Double = principal * (1 + rate / compoundsPerYear) ^ (compoundsPerYear * years) ' Display result LblFutureValue.Text = "Future Value: $" & Math.Round(amount, 2).ToString() End Sub
Output:

11.4 More Mathematical Applications
Here are additional formulas you can implement in VB2019:
1 Area of a Circle
area = Math.PI * radius ^ 2
2 Volume of a Cylinder
volume = Math.PI * radius ^ 2 * height
3 Fahrenheit to Celsius
celsius = (fahrenheit - 32) * 5 / 9
4 Miles to Kilometers
kilometers = miles * 1.60934
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned how to perform mathematical operations in Visual Basic 2019:
Arithmetic Operators
Mastered the use of +, -, *, /, ^, Mod, and \ operators
Practical Applications
Implemented real-world calculations like Pythagoras Theorem and BMI
Financial Formulas
Created a compound interest calculator
Unit Conversions
Learned formulas for temperature and distance conversions
Precision Control
Used Math.Round() to format numerical results
Mathematical operations are fundamental to building functional applications. In the next lesson, we'll explore string manipulation techniques for working with text data.
Next Lesson
Ready to learn about text manipulation? Continue to Lesson 12: String Manipulation.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 2019 Made Easy
Unlock the power of Visual Basic 2019 with this comprehensive, easy-to-follow handbook written by Dr. Liew, renowned educator and founder of the popular programming tutorial website VBtutor.net. Whether you're new to programming or brushing up your skills, this book is your perfect companion to learn Visual Basic 2019 from the ground up.
What You'll Learn:
- Understand Core Programming Concepts: Grasp the foundational principles of Visual Basic 2019, including variables, data types, conditional logic, loops, and event-driven programming.
- Develop Real Windows Desktop Applications: Build fully functional and interactive Windows apps using Visual Studio 2019—guided through step-by-step tutorials.
- Apply Dozens of Ready-to-Use Examples: Explore a rich collection of practical sample programs, from basic calculators to image viewers and database applications.
- Adapt and Reuse Code for Your Own Projects: Customize professionally written code snippets to speed up your development process and bring your ideas to life.
- Package and Deploy Like a Pro: Learn how to compile, test, and distribute your Visual Basic applications seamlessly with built-in deployment tools.

Visual Basic Programming With Code Examples
Visual Basic Programming with Code Examples offers a unique dual-format approach, showcasing sample codes in both Visual Basic 6 (VB6) and VB.NET. This side-by-side presentation helps you understand the evolution of Visual Basic and empowers you to work confidently across both environments.
What You'll Learn:
- Core Concepts Made Easy: Explore data types, control structures, file handling, procedures, user interface design, and more.
- Hands-On Application Building: Design real-world applications, including financial calculators, educational tools, games, multimedia apps, and database systems.
- 48 Practical Code Examples: Study and customize fully explained programs that illustrate key programming techniques.
- Dual-Code Format: Learn to translate and adapt code between VB6 and VB.NET seamlessly.