Lesson 25: Object-Oriented Programming
Master core OOP concepts in VB2019: encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism
Key Takeaway
Object-oriented programming (OOP) allows you to model real-world entities as software objects, making code more modular, reusable, and maintainable.
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is the foundation of Visual Basic 2019. In this lesson, we'll explore the three core OOP concepts: encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. These concepts enable you to create more organized, reusable, and maintainable code.
Encapsulation
Bundling data and methods into self-contained modules
Inheritance
Creating new classes based on existing ones
Polymorphism
Using a single interface for different data types
Modularity
Building applications from reusable components
25.1 Core OOP Concepts
In order for a programming language to qualify as an object-oriented programming language, it must have three core technologies: encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation refers to the creation of self-contained modules that bind processing functions to the data. These user-defined data types are called classes. Each class contains data as well as a set of methods which manipulate the data. The data components of a class are called instance variables and one instance of a class is an object.
For example, in a library system, a class could be a member, and John and Sharon could be two instances (two objects) of the library class.
Inheritance
Classes are created according to hierarchies, and inheritance allows the structure and methods in one class to be passed down the hierarchy. That means less programming is required when adding functions to complex systems. If a step is added at the bottom of a hierarchy, then only the processing and data associated with that unique step needs to be added. Everything else about that step is inherited.
Polymorphism
Object-oriented programming allows procedures about objects to be created whose exact type is not known until runtime. For example, a screen cursor may change its shape from an arrow to a line depending on the program mode. The routine to move the cursor on the screen in response to mouse movement would be written for "cursor," and polymorphism allows that cursor to take on whatever shape is required at runtime. It also allows new shapes to be easily integrated.
25.2 Creating Classes in VB2019
Visual Basic 2019 allows users to write programs that break down into modules. These modules represent real-world objects and are knows as classes or types. An object can be created out of a class and it is known as an instance of the class. A class can also comprise subclass.

Figure 25.1: Adding a class in VB2019
To create a class, start Visual Basic 2019 as usual and choose Windows Applications. In the Visual Basic 2019 IDE, click on Project on the menu bar and select Add Class.
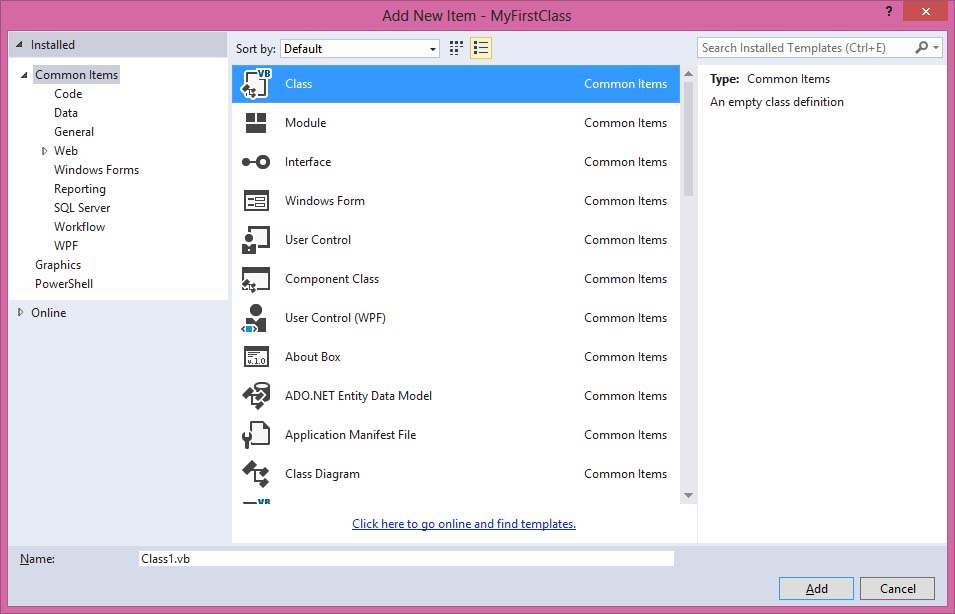
Figure 25.2: Add New Item dialog
Click on the Class item and the default class Class1.vb will appear as a new tab in a code window. Rename the class as MyClass.vb. Rename the form as MyFirstClass.vb.
Example: Creating a BMI Class
In the MyClass.vb window, create a new class MyClass1 with the following code:
Public Class MyClass1 Public Function BMI(ByVal height As Single, ByVal weight As Single) ' Calculate BMI using metric formula BMI = Format((weight) / (height ^ 2), "0.00") End Function End Class
Now you have created a class (an object) called MyClass1 with a method known as BMI that calculates Body Mass Index.
25.3 Using Classes in Your Application
In order to use the BMI class, insert a button into the form and add the following code to the button's click event:
Private Sub BtnBMI_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnBMI.Click ' Create an instance of the MyClass1 Dim MyObject As Object Dim h, w As Single ' Instantiate the class MyObject = New MyClass1() ' Get user input h = InputBox("What is your height in meter") w = InputBox("What is your weight in kg") ' Call the BMI method and display result MessageBox.Show(MyObject.BMI(h, w), "Your BMI") End Sub
When you run this program and click the button, the user will be presented with two input boxes to enter height and weight. The BMI value will then be shown in a message box.
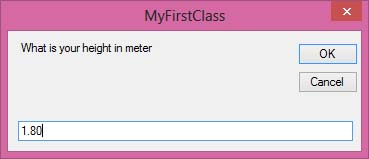
Figure 25.3: Input height
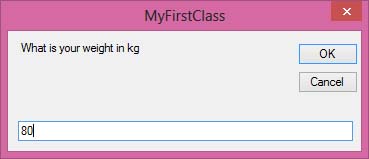
Figure 25.4: Input weight
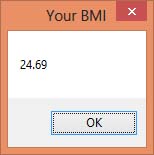
Figure 25.5: BMI calculation result
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned the fundamentals of object-oriented programming in VB2019:
OOP Concepts
Understand encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism
Class Creation
Create classes with properties and methods
Object Instantiation
Create objects from classes and use their methods
Practical Example
Implement a BMI calculator using OOP principles
Object-oriented programming is essential for creating scalable, maintainable applications. In the next lesson, we'll explore graphics programming in VB2019.
Next Lesson
Learn to create graphics in Lesson 26: Introduction to Graphics.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 2019 Made Easy
Unlock the power of Visual Basic 2019 with this comprehensive, easy-to-follow handbook written by Dr. Liew, renowned educator and founder of the popular programming tutorial website VBtutor.net. Whether you're new to programming or brushing up your skills, this book is your perfect companion to learn Visual Basic 2019 from the ground up.
What You'll Learn:
- Understand Core Programming Concepts: Grasp the foundational principles of Visual Basic 2019, including variables, data types, conditional logic, loops, and event-driven programming.
- Develop Real Windows Desktop Applications: Build fully functional and interactive Windows apps using Visual Studio 2019—guided through step-by-step tutorials.
- Apply Dozens of Ready-to-Use Examples: Explore a rich collection of practical sample programs, from basic calculators to image viewers and database applications.
- Adapt and Reuse Code for Your Own Projects: Customize professionally written code snippets to speed up your development process and bring your ideas to life.
- Package and Deploy Like a Pro: Learn how to compile, test, and distribute your Visual Basic applications seamlessly with built-in deployment tools.

Visual Basic Programming With Code Examples
Visual Basic Programming with Code Examples offers a unique dual-format approach, showcasing sample codes in both Visual Basic 6 (VB6) and VB.NET. This side-by-side presentation helps you understand the evolution of Visual Basic and empowers you to work confidently across both environments.
What You'll Learn:
- Core Concepts Made Easy: Explore data types, control structures, file handling, procedures, user interface design, and more.
- Hands-On Application Building: Design real-world applications, including financial calculators, educational tools, games, multimedia apps, and database systems.
- 48 Practical Code Examples: Study and customize fully explained programs that illustrate key programming techniques.
- Dual-Code Format: Learn to translate and adapt code between VB6 and VB.NET seamlessly.