Lesson 35: Connecting Database in VB2019
Learn to establish database connections and retrieve data using ADO.NET
Key Takeaway
Learn to establish database connections using ADO.NET objects and retrieve data efficiently.
In this lesson, we'll build upon the database fundamentals covered in Lesson 34 to establish actual database connections in VB2019. You'll learn how to use ADO.NET objects to connect to SQL Server databases and retrieve data for your applications.
SqlConnection
Establish connections to SQL Server databases
SqlDataAdapter
Populate DataTables with database records
DataTable
Store and manipulate database records locally
SqlCommandBuilder
Generate commands for data manipulation
35.1 Creating Database Connection with ADO.NET
To connect to a database in Visual Basic 2019, we need to create a connection object before accessing data. We'll use SQL Server as our database engine and create a database named test.mdf with a table called Contacts.
Figure 35.1: Creating the Contacts table in SQL Server
ADO.NET Connection Objects
ADO.NET provides several connection objects:
| Connection Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| SqlConnection | Connects to Microsoft SQL Server databases | SQL Server databases |
| OleDbConnection | Connects to OLEDB data sources | Microsoft Access databases |
| OdbcConnection | Connects via ODBC drivers | Legacy database systems |
Since we're working with SQL Server, we'll use the SqlConnection object:
Private MyCn As New SqlConnection
Connection String
After creating the SqlConnection instance, we establish the connection using the ConnectionString property:
MyCn.ConnectionString = "Data Source=.\SQLEXPRESS; " & _ "AttachDbFilename=C:\Documents\vb2019\data\Test.mdf; " & _ "User Instance=True;Integrated Security=True;" & _ "Connection Timeout=30;"
Important: You'll need to modify the SQL server reference and database file path to match your environment.
After establishing the connection, open the database:
MyCn.Open()
35.2 Populating Data with ADO.NET
Establishing a database connection alone isn't sufficient to work with data. We need additional ADO.NET objects to retrieve and manipulate data.
Essential ADO.NET Objects
Private MyDatAdp As New SqlDataAdapter Private MyCmdBld As New SqlCommandBuilder Private MyDataTbl As New DataTable Private MyRowPosition As Integer = 0
In the Form_Load event, we populate the DataTable:
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load MyDatAdp = New SqlDataAdapter("Select * from Contacts", MyCn) MyCmdBld = New SqlCommandBuilder(MyDatAdp) MyDatAdp.Fill(MyDataTbl) ' Display first record Dim MyDataRow As DataRow = MyDataTbl.Rows(0) TxtName.Text = MyDataRow("ContactName").ToString() TxtState.Text = MyDataRow("State").ToString() ' Show all records showRecords() End Sub
Displaying Records
We create a showRecords subroutine to display data in text boxes:
Private Sub showRecords() If MyDataTbl.Rows.Count = 0 Then TxtName.Text = "" TxtState.Text = "" Exit Sub End If TxtName.Text = MyDataTbl.Rows(MyRowPosition)("ContactName").ToString() TxtState.Text = MyDataTbl.Rows(MyRowPosition)("State").ToString() End Sub
Complete Implementation
Here's the complete code for connecting to the database and displaying records:
Public Class Form1 Private MyDatAdp As New SqlDataAdapter Private MyCmdBld As New SqlCommandBuilder Private MyDataTbl As New DataTable Private MyCn As New SqlConnection Private MyRowPosition As Integer = 0 Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load MyCn.ConnectionString = "Data Source=TOSHIBA-PC\SQL2017; " & _ "AttachDbFilename=C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\" & _ "MSSQL11.SQL2017\MSSQL\DATA\Test.mdf; " & _ "User Instance=True;Integrated Security=SSPI" MyCn.Open() MyDatAdp = New SqlDataAdapter("Select * from Contacts", MyCn) MyCmdBld = New SqlCommandBuilder(MyDatAdp) MyDatAdp.Fill(MyDataTbl) ' Display first record Dim MyDataRow As DataRow = MyDataTbl.Rows(0) TxtName.Text = MyDataRow("ContactName").ToString() TxtState.Text = MyDataRow("State").ToString() showRecords() End Sub Private Sub showRecords() If MyDataTbl.Rows.Count = 0 Then TxtName.Text = "" TxtState.Text = "" Exit Sub End If TxtName.Text = MyDataTbl.Rows(MyRowPosition)("ContactName").ToString() TxtState.Text = MyDataTbl.Rows(MyRowPosition)("State").ToString() End Sub End Class
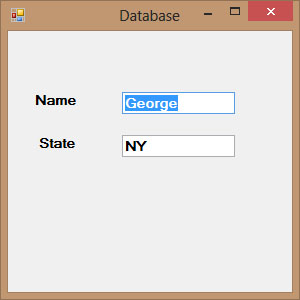
Figure 35.2: Displaying database records in a VB2019 application
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned how to connect VB2019 applications to SQL Server databases:
Database Connection
Using SqlConnection to establish database connections
Data Retrieval
Using SqlDataAdapter to retrieve data from databases
Data Storage
Storing records in DataTable objects for manipulation
Record Display
Displaying database records in application UI
In the next lesson, we'll learn how to navigate through records and edit database data.
Next Lesson
Learn to navigate and edit database records in Lesson 36: Editing Database Data.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 2019 Made Easy
Master Visual Basic 2019 with this comprehensive guide that includes detailed coverage of database programming techniques. Learn to create professional database applications.
Key Database Topics:
- Database fundamentals and concepts
- SQL Server setup and configuration
- ADO.NET programming techniques
- Data binding and manipulation
- Practical database projects with source code

Database Programming with VB.NET
This comprehensive guide focuses specifically on database programming techniques in VB.NET, covering everything from basic concepts to advanced techniques.
Database Coverage:
- In-depth ADO.NET coverage
- SQL Server integration
- Entity Framework
- Real-world database application examples