Lesson 17: Creating Functions in VB2019
Master the art of creating reusable functions that return values
Key Takeaway
Functions allow you to encapsulate reusable logic that returns a value, making your code more organized, modular, and maintainable.
In this lesson, we'll explore how to create user-defined functions in Visual Basic 2019. Functions are similar to sub procedures but with one major difference - they return values. We'll cover the syntax for creating functions, demonstrate practical examples, and explain how to pass arguments by value and by reference.
17.1 Creating User-Defined Functions
A function is a block of code that performs a specific task and returns a value. Functions help break down complex problems into smaller, manageable parts and promote code reuse.
Function Syntax
Public Function functionName(parameters) As returnType
' Code to execute
Return value
End Function
Or:
Private Function functionName(parameters) As returnType
' Code to execute
Return value
End Function
The Public keyword makes the function accessible throughout the project, while Private restricts it to the current module. The As returnType specifies the data type of the value the function returns.
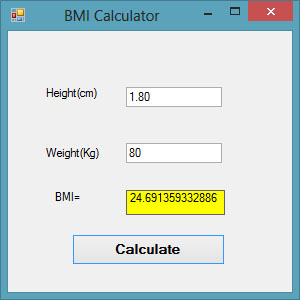
17.1(a) BMI Calculator
This example demonstrates a function that calculates Body Mass Index (BMI) based on height and weight. BMI is calculated using the formula: weight / (height)2, where weight is in kilograms and height is in meters.
Public Class Form1 Private Function BMI(Height As Single, weight As Single) As Double BMI = weight / Height ^ 2 End Function Private Sub BtnCal_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCal.Click Dim h As Single, w As Single h = Val(TextBox1.Text) w = Val(TextBox2.Text) LblBMI.Text = BMI(h, w) End Sub End Class
Output:
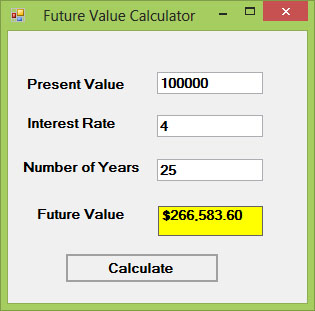
17.1(b) Future Value Calculator
This example demonstrates a function that calculates the future value of an investment based on compound interest. The formula used is: FV = PV * (1 + i / 100)n, where PV is the present value, i is the interest rate, and n is the number of periods.
Public Class Form1 Private Function FV(pv As Single, i As Single, n As Integer) As Double FV = pv * (1 + i / 100) ^ n End Function Private Sub BtnCal_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCal.Click Dim FutureVal As Single Dim PresentVal As Single Dim interest As Single Dim period As Integer PresentVal = TxtPV.Text interest = TxtInt.Text period = TxtN.Text FutureVal = FV(PresentVal, interest, period) LblFV.Text = Format(FutureVal, "$#,##0.00") End Sub End Class
Output:
17.2 Passing Arguments by Value and by Reference
In Visual Basic, you can pass arguments to functions either by value or by reference. This affects whether the function can modify the original variable passed to it.
ByVal (By Value)
Creates a copy of the argument. Changes made to the parameter inside the function don't affect the original variable.
ByRef (By Reference)
Passes a reference to the original variable. Changes made to the parameter inside the function affect the original variable.
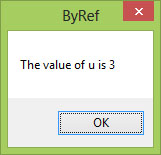
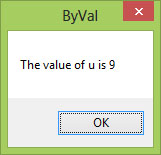
17.2(a) ByVal vs ByRef Demonstration
This example demonstrates the difference between passing arguments by value (ByVal) and by reference (ByRef).
Public Class Form1 Private Function sqroot(ByRef x As Single) As Double x = x ^ 0.5 sqroot = x End Function Private Function sqroot1(ByVal y As Single) As Double y = y ^ 0.5 sqroot1 = y End Function Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Dim u As Single u = 9 MsgBox(3 * sqroot(u), , "ByRef") MsgBox("Value of u is " & u, , "ByRef") End Sub Private Sub Button2_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click Dim u As Single u = 9 MsgBox(3 * sqroot1(u), , "ByVal") MsgBox("Value of u is " & u, , "ByVal") End Sub End Class
Output:
17.3 Benefits of Using Functions
Code Reusability
Write once, use multiple times throughout your application without duplicating code
Modularity
Break complex problems into smaller, manageable pieces that are easier to understand
Easier Debugging
Isolate and test individual components of your application more effectively
Return Values
Provide results that can be used in expressions and assignments throughout your code
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned how to create and use functions in Visual Basic 2019 to organize your code and create modular applications:
Function Structure
Mastered the syntax for creating functions with parameters and return types
Practical Applications
Implemented BMI and Future Value calculators using functions
Argument Passing
Understood the difference between ByVal and ByRef parameter passing
Code Organization
Learned how functions promote modular programming for maintainability
Functions are fundamental for creating well-organized, maintainable applications that can return values. By breaking your code into logical units that produce results, you can create applications that are easier to understand, debug, and extend. In the next lesson, we'll explore built-in math functions.
Next Lesson
Ready to learn about built-in math functions? Continue to Lesson 18: Math Functions.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 2019 Made Easy
Unlock the power of Visual Basic 2019 with this comprehensive, easy-to-follow handbook written by Dr. Liew, renowned educator and founder of the popular programming tutorial website VBtutor.net. Whether you're new to programming or brushing up your skills, this book is your perfect companion to learn Visual Basic 2019 from the ground up.
What You'll Learn:
- Understand Core Programming Concepts: Grasp the foundational principles of Visual Basic 2019, including variables, data types, conditional logic, loops, and event-driven programming.
- Develop Real Windows Desktop Applications: Build fully functional and interactive Windows apps using Visual Studio 2019—guided through step-by-step tutorials.
- Apply Dozens of Ready-to-Use Examples: Explore a rich collection of practical sample programs, from basic calculators to image viewers and database applications.
- Adapt and Reuse Code for Your Own Projects: Customize professionally written code snippets to speed up your development process and bring your ideas to life.
- Package and Deploy Like a Pro: Learn how to compile, test, and distribute your Visual Basic applications seamlessly with built-in deployment tools.

Visual Basic Programming With Code Examples
Visual Basic Programming with Code Examples offers a unique dual-format approach, showcasing sample codes in both Visual Basic 6 (VB6) and VB.NET. This side-by-side presentation helps you understand the evolution of Visual Basic and empowers you to work confidently across both environments.
What You'll Learn:
- Core Concepts Made Easy: Explore data types, control structures, file handling, procedures, user interface design, and more.
- Hands-On Application Building: Design real-world applications, including financial calculators, educational tools, games, multimedia apps, and database systems.
- 48 Practical Code Examples: Study and customize fully explained programs that illustrate key programming techniques.
- Dual-Code Format: Learn to translate and adapt code between VB6 and VB.NET seamlessly.