Lesson 11: Mastering Mathematical Functions in VB6
Learn to use Rnd, Int, Sqr, Abs, Exp, Fix, Round, and Log with practical examples
Key Takeaway
Mathematical functions in VB6 enable you to perform complex calculations, generate random numbers, and solve mathematical problems efficiently in your applications.
Welcome to Lesson 11 of our Visual Basic 6 Tutorial! In this lesson, you'll master VB6's essential mathematical functions. These functions are crucial for creating applications that involve calculations, simulations, games, and data analysis.
11.1 The Rnd Function: Random Number Generation
The Rnd function is essential for applications involving probability, simulations, games, and random selections. It returns a random Single value between 0 (inclusive) and 1 (exclusive).
Important Note
Always use Randomize before calling Rnd to ensure different random sequences each time your program runs. Without it, you'll get the same sequence of "random" numbers every time!
Example 11.1: Generating Random Numbers
Private Sub Form_Activate() Dim x As Integer Randomize ' Initialize random number generator For x = 1 To 10 Print Rnd Next x End Sub
Random Numbers Output:
Practical Application: Simulating Dice Rolls
To create useful random numbers, we often need to scale and convert the output of Rnd. The formula for generating random integers in a specific range is:
Int((upperbound - lowerbound + 1) * Rnd + lowerbound)
For a 6-sided die (values 1-6), the formula becomes:
Int(Rnd * 6) + 1
Example 11.2: Virtual Die Simulator
Dim num As Integer Private Sub cmdRoll_Click() Randomize num = Int(Rnd * 6) + 1 lblDie.Caption = num End Sub
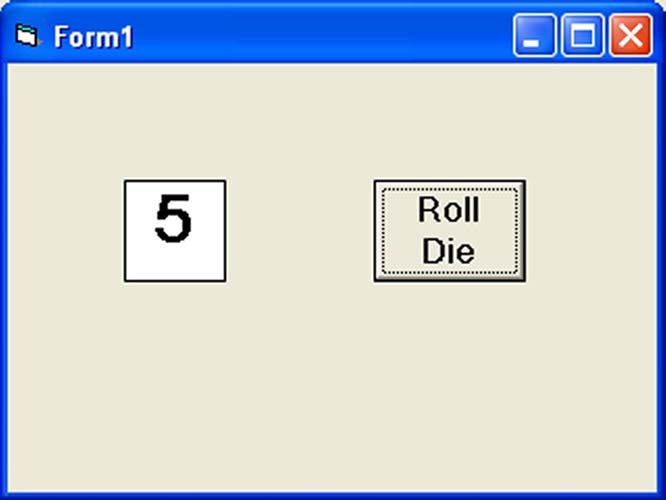
Figure 11.1: Virtual die showing a roll result of 3
11.2 Essential Numeric Functions
VB6 provides a comprehensive set of mathematical functions for various operations. Understanding these functions is crucial for efficient programming.
Rounding Functions
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Int | Largest integer ≤ number | Int(4.8)=4 Int(-4.3)=-5 |
| Fix | Integer portion of number | Fix(4.8)=4 Fix(-4.3)=-4 |
| Round | Rounds to specified decimals | Round(3.14159,2)=3.14 |
Calculation Functions
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Sqr | Square root | Sqr(16)=4 |
| Abs | Absolute value | Abs(-7.25)=7.25 |
Exponential Functions
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Exp | e raised to a power | Exp(1)=2.71828 |
| Log | Natural logarithm | Log(10)≈2.302585 |
Example 11.3: Comparing Int, Fix, and Round
Private Sub Form_Activate() Dim n As Integer Dim x As Single Print "n", "x", "Int(x)", "Fix(x)", "Round(x, 4)" For n = 1 To 10 x = Round(Rnd * 7, 7) Print n, x, Int(x), Fix(x), Round(x, 4) Next n End Sub

Figure 11.2: Comparing Int, Fix, and Round functions
Key Differences: Int vs Fix
1 Int Function
- Returns the largest integer ≤ the number
- For positive numbers: truncates decimals
- For negative numbers: rounds down to next lower integer
- Int(7.8) = 7
- Int(-7.2) = -8
2 Fix Function
- Returns the integer portion of a number
- For positive numbers: same as Int
- For negative numbers: truncates decimals (rounds toward zero)
- Fix(7.8) = 7
- Fix(-7.2) = -7
New Example: Hypotenuse Calculator
Private Sub cmdCalculateHyp_Click() Dim a As Double, b As Double, c As Double ' Get user input a = Val(InputBox("Enter length of side A:", "Right Triangle")) b = Val(InputBox("Enter length of side B:", "Right Triangle")) ' Calculate hypotenuse using Pythagorean theorem If a > 0 And b > 0 Then c = Round(Sqr(a ^ 2 + b ^ 2), 2) MsgBox "Hypotenuse = " & c, vbInformation, "Result" Else MsgBox "Please enter positive numbers", vbExclamation, "Error" End If End Sub
Explanation: This example uses Val for conversion, Sqr for square root, ^ for exponents, and Round for precision. It also demonstrates input validation.
Math Function Simulator
Test different mathematical functions with custom inputs
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've mastered VB6's essential mathematical functions:
Rnd Function
Generate random numbers for simulations and games
Rounding Functions
Int, Fix, and Round for different rounding scenarios
Calculation Functions
Sqr for square roots, Abs for absolute values
Exponential Functions
Exp for exponentials, Log for natural logarithms
Randomize
Essential for initializing the random number generator
Best Practice
Always validate inputs before performing mathematical operations. For example, check for negative numbers before using Sqr, and verify numbers are within the valid range for Log.
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of VB6 mathematical functions with these exercises:
Exercise 1: Random Password Generator
Create a program that generates a random 8-character password containing uppercase letters (A-Z). Use Chr() and Rnd together (A-Z characters are ASCII 65-90).
Exercise 2: Quadratic Equation Solver
Create a program that solves quadratic equations (ax² + bx + c = 0). Use Sqr for the discriminant and handle cases with real and complex roots.
Exercise 3: Compound Interest Calculator
Calculate compound interest using the formula A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt). Use Exp and Log for continuous compounding option.
Exercise 4: Statistics Calculator
Create a program that calculates the mean and standard deviation of 10 random numbers between 1 and 100. Use Sqr for standard deviation.
Exercise 5: Geometry Calculator
Create a program that calculates the volume of different shapes (sphere, cylinder, cone) based on user input. Use Round for precision.
Next Lesson
Continue your VB6 journey with Lesson 12: Formatting Functions.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 6 Made Easy
The ultimate beginner-friendly guide for mastering Windows-based application development using Visual Basic 6. Used as a textbook by universities worldwide.
What You'll Learn:
- Comprehensive coverage of VB6 coding techniques
- Event-driven programming best practices
- Practical examples and projects
- Debugging and error handling
- Database integration
- Advanced UI development

Visual Basic 2022 Made Easy
The ultimate guide to VB.NET programming in Visual Studio 2022. Master modern VB development with this comprehensive resource.
What You'll Learn:
- Modern VB.NET coding techniques
- Visual Studio 2022 features
- Advanced UI development
- Database programming with ADO.NET
- Web API integration
- Deployment strategies