Lesson 15: Excel VBA Functions
Learn how to create custom functions in Excel using VBA to enhance spreadsheet capabilities
Key Takeaway
Excel VBA functions allow you to create custom calculations that extend Excel's built-in capabilities, enabling powerful solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Welcome to Lesson 15 of our Visual Basic 6 Tutorial! In this lesson, you'll learn how to create custom functions in Excel using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). These user-defined functions complement Excel's built-in functions and provide flexible solutions to complex problems.
15.1 Creating Excel VBA Functions
We can enhance the capabilities of MS Excel spreadsheets by creating customized functions to complement the built-in functions. While the built-in functions have certain limitations, these user-defined functions, also known as Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) functions aka macros, provide flexible and powerful solutions.
Commission Payment Structure
Table 15.1 shows the commission rates based on sales volume
| Sales Volume($) | Commissions |
|---|---|
| <500 | 3% |
| <1000 | 6% |
| <2000 | 9% |
| <5000 | 12% |
| >5000 | 15% |
For example, when a salesman attains a sale volume of $6000, they will be paid $6000 × 15% = $720.00.
Commission Calculation Function
A VBA function to calculate commissions based on the above structure can be written as follows:
Function Comm(Sales_V As Variant) As Variant If Sales_V < 500 Then Comm = Sales_V * 0.03 ElseIf Sales_V >= 500 And Sales_V < 1000 Then Comm = Sales_V * 0.06 ElseIf Sales_V >= 1000 And Sales_V < 2000 Then Comm = Sales_V * 0.09 ElseIf Sales_V >= 2000 And Sales_V < 5000 Then Comm = Sales_V * 0.12 ElseIf Sales_V >= 5000 Then Comm = Sales_V * 0.15 End If End Function
Commission Calculator:
Function Structure
VBA functions follow the same structure as regular VB functions but are specifically designed to work within Excel. They can accept parameters and return values that can be used directly in Excel formulas.
15.2 Using Microsoft Excel Visual Basic Editor
To create VBA functions in MS Excel, you can click on Tools, select Macro and then click on Visual Basic Editor as shown in Figure 15.1:
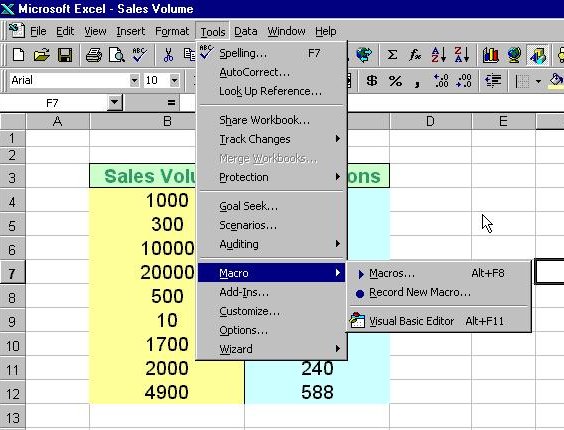
Upon clicking the Visual Basic Editor, the VB Editor windows will appear as shown in Figure 15.2. To create a function, type in the function as illustrated in section 15.1 above. After typing, save the file and then return to the Excel windows.

Using the Custom Function in Excel
In the Excel window, type in the titles Sales Volume and Commissions in any two cells. By referring to figure 15.3, key-in the Comm function at cell C4 and by referencing the value in cell B4, using the format Comm(B4). Any value appearing in cell B4 will pass the value to the Comm function in cell C4.
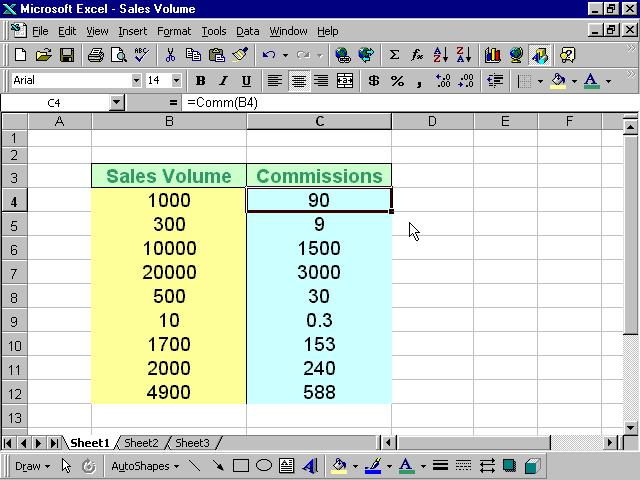
For the rest of the rows, just copy the formula by dragging the bottom right corner of cell C4 to the required cells. A nice and neat table that shows the commissions will automatically appear. It can also be updated anytime.
1 Create Function
Write your custom function in the VBA Editor using the same syntax as VB6 functions.
2 Save Workbook
Save your Excel workbook as a macro-enabled file (.xlsm) to preserve your VBA code.
3 Use in Spreadsheet
Call your function in any cell just like a built-in Excel function (e.g., =Comm(B4)).
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned how to create and use custom Excel VBA functions:
Custom Functions
Create VBA functions to extend Excel's capabilities
VB Editor
Access and use the Visual Basic Editor in Excel
Practical Application
Implement custom functions in spreadsheets
Maintenance
Update and maintain custom functions
Best Practice
Always save your Excel workbooks with custom VBA functions as macro-enabled files (.xlsm) to preserve your code. Use descriptive function names and include comments to make your code maintainable.
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of Excel VBA functions with these exercises:
Exercise 1: Tax Calculator
Create a VBA function that calculates tax based on income brackets.
Exercise 2: Discount Function
Develop a function that applies tiered discounts based on purchase amount.
Exercise 3: Grade Calculator
Create a function that converts numerical scores to letter grades.
Exercise 4: Shipping Cost Calculator
Build a function that calculates shipping costs based on weight and destination.
Exercise 5: Date Formatter
Create a function that formats dates in a custom format for reports.
Further Learning
To learn more about Excel VBA, check out our comprehensive Excel VBA Tutorial for in-depth guides and examples.
Next Lesson
Continue your VB6 journey with Lesson 16: Arrays.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 6 Made Easy
The ultimate beginner-friendly guide for mastering Windows-based application development using Visual Basic 6. Used as a textbook by universities worldwide.
What You'll Learn:
- Comprehensive coverage of VB6 coding techniques
- Event-driven programming best practices
- Practical examples and projects
- Debugging and error handling
- Database integration
- Advanced UI development

Mastering Excel VBA 365
Master Excel automation with this comprehensive guide to VBA programming. Learn to create powerful macros and custom functions.
What You'll Learn:
- Automate repetitive tasks
- Create custom Excel functions
- Develop user forms and interfaces
- Work with Excel objects
- Error handling techniques
- Real-world application development