Lesson 26: Managing Database Using DataGrid Control
Learn to display and edit database records efficiently with the powerful DataGrid control
Key Takeaway
The DataGrid control provides an efficient way to display and edit entire database recordsets in a spreadsheet-like format, making it ideal for managing database content.
Welcome to Lesson 26 of our Visual Basic 6 Tutorial! In this lesson, you'll learn how to manage databases using the DataGrid control, which offers a powerful way to display and edit entire database recordsets in a tabular format. Unlike textboxes that display one record at a time, the DataGrid shows multiple records simultaneously.
26.1 Introduction to DataGrid Control
The DataGrid control is a powerful component for database applications that allows users to:
Display Entire Recordsets
Show multiple database records at once
Edit Records Directly
Modify data directly in the grid interface
Navigate Records
Scroll through large datasets easily
26.1.1 Adding DataGrid Control to Toolbox
To use the DataGrid control, you need to add it to your toolbox:
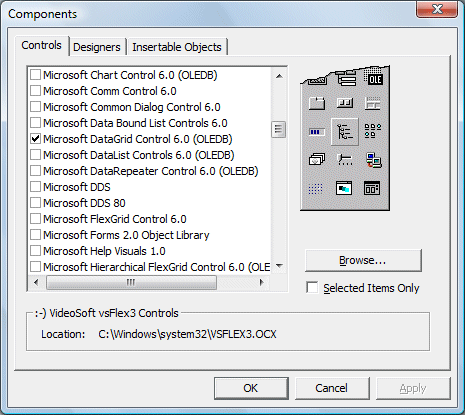
1Open Components Dialog
Press Ctrl+T to open the Components dialog box
2Select Controls
Check Microsoft DataGrid Control 6.0 and Microsoft ADO Data Control 6.0
3Confirm
Click OK to add controls to your toolbox
26.2 Building a Library Database Application
We'll create a book database application to demonstrate DataGrid capabilities. First, create a database file using Microsoft Access named books.mdb with a table named book containing fields like ISBN, Title, Author, Year, etc.

26.2.1 Designing the Interface
After adding the DataGrid and ADO controls to your form:


26.3 Connecting to Database
To connect ADO to the database file:
1Set ConnectionString
Right-click ADO control, open properties, and set ConnectionString
2Select Database
Click Build, choose database provider, and select your database file
3Set RecordSource
In RecordSource tab, set Command Type to adCmdTable and Table to book



26.4 Configuring DataGrid Properties
After connecting the database to ADO, configure the DataGrid:
DataSource Property
Set to the name of your ADO control (e.g., Adodc1)
AllowAddNew Property
Set to True to allow users to add new records
AllowDelete Property
Set to True to allow users to delete records
AllowUpdate Property
Set to True to allow users to edit existing records

26.5 DataGrid Programming Techniques
While the DataGrid provides many features without code, you can enhance it with programming:
26.5.1 Refreshing Data
Private Sub cmdRefresh_Click() Adodc1.Refresh DataGrid1.Refresh End Sub
26.5.2 Customizing Columns
Private Sub Form_Load() ' Set column widths DataGrid1.Columns(0).Width = 1200 ' ISBN DataGrid1.Columns(1).Width = 3000 ' Title DataGrid1.Columns(2).Width = 2000 ' Author ' Set column headers DataGrid1.Columns(0).Caption = "ISBN Number" DataGrid1.Columns(1).Caption = "Book Title" DataGrid1.Columns(2).Caption = "Author" End Sub
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned how to manage databases using DataGrid Control in VB6:
DataGrid Advantages
Efficient display and editing of entire recordsets
Setup Process
Adding DataGrid control to toolbox and connecting to databases
Database Connection
Configuring ADO control and DataGrid properties
Programming Techniques
Customizing columns and refreshing data programmatically
Important Note
The DataGrid control provides a spreadsheet-like interface that significantly simplifies database management compared to using multiple textboxes for each field.
Practice Exercises
Enhance your DataGrid application with these exercises:
Exercise 1: Column Formatting
Customize the appearance of your DataGrid columns (widths, headers, alignment)
Exercise 2: Search Function
Add a search feature to filter records in the DataGrid
Exercise 3: Record Validation
Implement validation for DataGrid edits to prevent invalid data
Exercise 4: Data Export
Add functionality to export DataGrid content to a CSV file
Exercise 5: Sorting
Implement column header click sorting functionality
Next Lesson
Continue your VB6 journey with Lesson 27: SQL Queries.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 6 Made Easy
The ultimate beginner-friendly guide for mastering Windows-based application development using Visual Basic 6. Used as a textbook by universities worldwide.
What You'll Learn:
- Comprehensive coverage of VB6 coding techniques
- Database application development
- Practical examples and projects
- Debugging and error handling
- Advanced database integration
- Professional UI development

Visual Basic 2022 Made Easy
The ultimate guide to VB.NET programming in Visual Studio 2022. Master modern VB development with this comprehensive resource.
What You'll Learn:
- Modern VB.NET coding techniques
- Visual Studio 2022 features
- Database programming with ADO.NET
- Advanced UI development
- Entity Framework integration
- Deployment strategies