Lesson 2: Creating Visual Basic 6 Applications
Learn how to build your first VB6 application with step-by-step instructions and practical examples
Key Takeaway
Building a VB6 application involves two main steps: designing the interface and writing the event-driven code. The VB6 IDE provides all the tools needed to create Windows applications efficiently.
Welcome to Lesson 2 of our Visual Basic 6 Tutorial! In this lesson, you'll learn how to create your first VB6 application from scratch. We'll cover everything from launching the IDE to writing functional code for interactive applications.
2.1 Creating Your First Application
1 Launching the VB6 IDE
Start the Microsoft Visual Basic 6 compiler. In the New Project dialog, select Standard EXE to enter the Visual Basic 6 Integrated Development Environment (IDE). A default form named Form1 will appear.
2 Accessing the Code Window
Double-click on Form1 to open its source code window, as shown below. This is where you'll write your VB6 code.
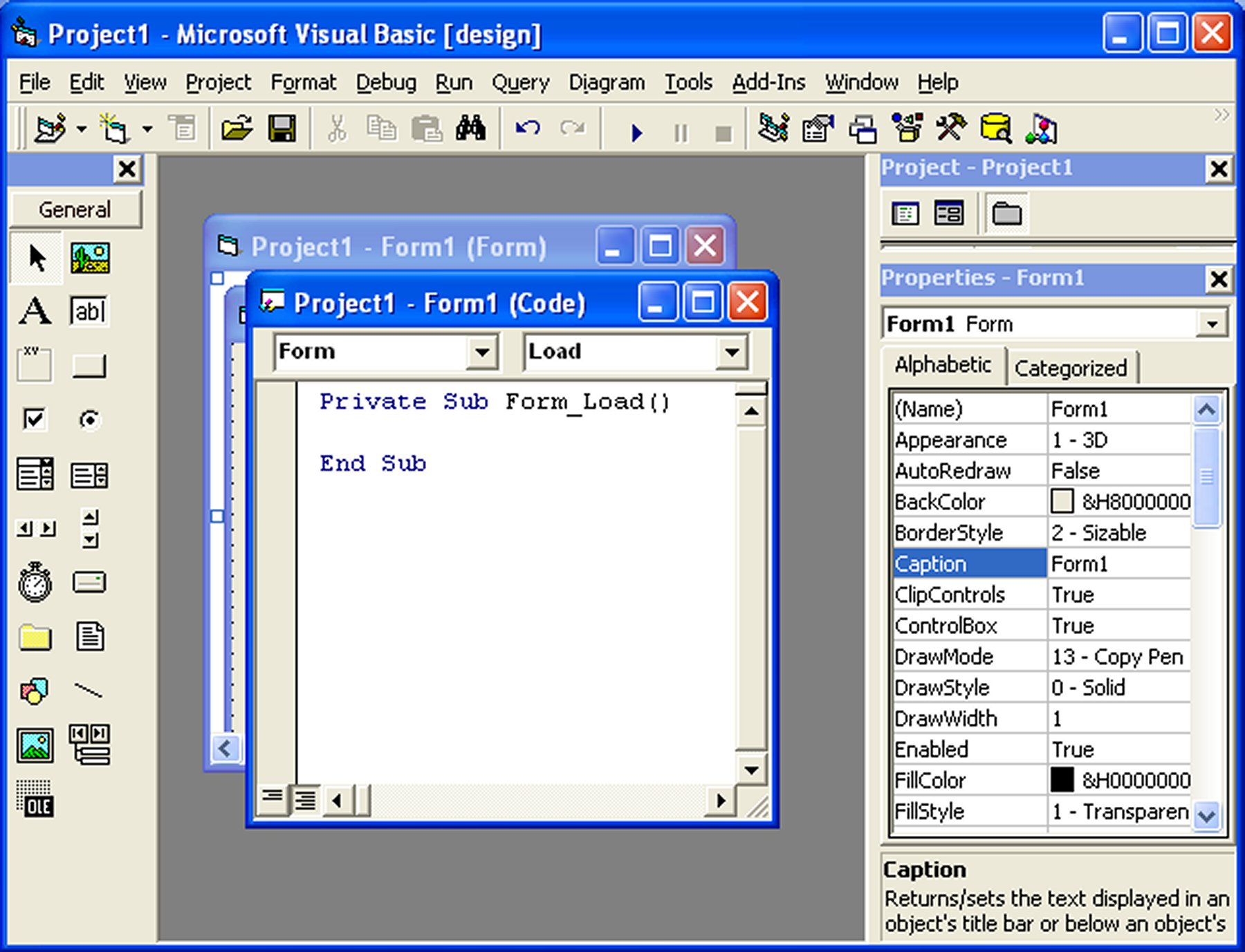
Understanding the Object and Procedure Boxes
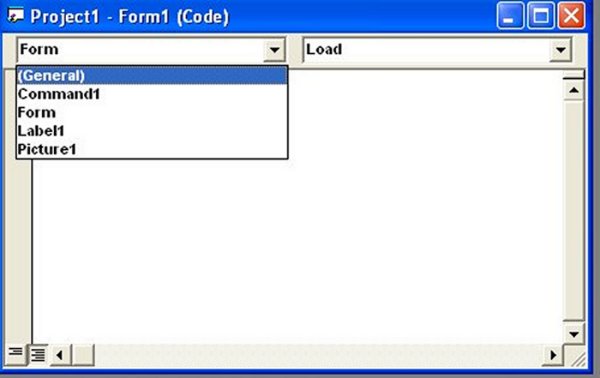
At the top of the code window, you'll find two drop-down lists:
Object Box
Displays the objects on your form (e.g., Form1, Command1, Label1)
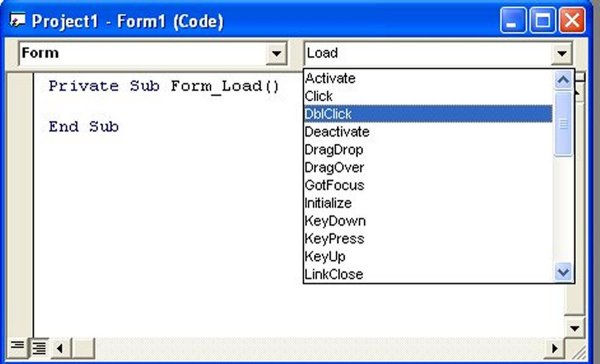
Procedure Box
Shows events associated with the selected object (e.g., Load, Click, DblClick)
Writing Your First Code
You don't need to worry about the Private Sub and End Sub statements; just enter your code between them. For example:
Private Sub Form_Load() Form1.show Print "Welcome to Visual Basic tutorial" End Sub
Output:
Running this code (press F5) will display the message in the form:

Performing Arithmetic Operations
You can perform arithmetic calculations using the Print statement:
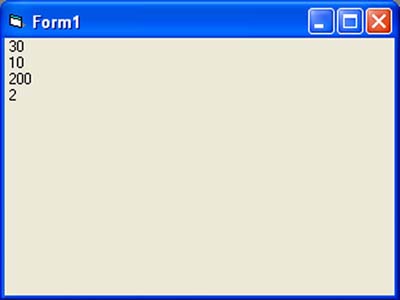
Private Sub Form_Activate() Print 20 + 10 Print 20 - 10 Print 20 * 10 Print 20 / 10 End Sub
Output:
Press F5 or click the run button to see the results arranged vertically:
Concatenating Strings
Use the + or & operator to join strings:
Using + Operator
Concatenates strings but can cause errors with mixed types
Using & Operator
Safer method that converts non-strings to strings
Private Sub Form_Load() Dim A, B, C, D, E As String A = "Tom" B = "likes" C = "to" D = "eat" E = "burger" ' Using + operator Print A + B + C + D + E ' Using & operator Print A & B & C & D & E End Sub
Output:
The output of both concatenation methods:

2.2 Steps in Building a Visual Basic Application
1 Design the Interface
- Add controls (e.g., buttons, labels) to the form
- Set their properties (e.g., Caption, BackColor, Font)
2 Write Event Procedures
- Double-click on a control to open its code window
- Write code that defines behavior during events
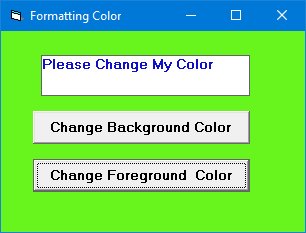
Example: Changing Colors Randomly
Create a form with two command buttons and a label:
Command1
Changes the background color
Command2
Changes the foreground color
Label1
Displays the current foreground color
We'll use the Rnd(), Int(), and RGB() functions to generate random colors.
Private Sub Command1_Click() ' Change form background color randomly Randomize Dim R As Integer = Int(Rnd() * 256) Dim G As Integer = Int(Rnd() * 256) Dim B As Integer = Int(Rnd() * 256) Form1.BackColor = RGB(R, G, B) End Sub Private Sub Command2_Click() ' Change label foreground color randomly Randomize Dim R As Integer = Int(Rnd() * 256) Dim G As Integer = Int(Rnd() * 256) Dim B As Integer = Int(Rnd() * 256) Label1.ForeColor = RGB(R, G, B) Label1.Caption = "Foreground Color Changed" End Sub
Output:
Running this program allows users to change colors randomly:
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned how to create your first VB6 applications:
IDE Navigation
Launched the VB6 IDE and accessed the code window
Basic Programming
Displayed messages, performed arithmetic, and concatenated strings
Application Structure
Understood the two-step process of building VB6 applications
Interactive Features
Created a color-changing application with random color generation
You've now built functional VB6 applications and are ready to explore more advanced topics in the next lesson.
Next Lesson
Ready to learn how to work with VB6 controls? Continue to Lesson 3: Working with Controls.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 6 Made Easy
The ultimate beginner-friendly guide for mastering Windows-based application development using Visual Basic 6. Used as a textbook by universities worldwide.
What You'll Learn:
- Introduction to the VB6 IDE
- Working with variables and data types
- Designing forms and interfaces
- Using controls like buttons and text boxes
- Creating database applications
- Debugging and error handling techniques

Visual Basic 2022 Made Easy
The ultimate guide to VB.NET programming in Visual Studio 2022. Master modern VB development with this comprehensive resource.
What You'll Learn:
- Visual Studio 2022 IDE fundamentals
- Variables, data types, and procedures
- Designing modern Windows applications
- Database programming with ADO.NET
- Web API integration
- Advanced debugging techniques