Lesson 4: Writing the Code in VB6
Master VB6 coding techniques to create interactive applications with professional event handling
Key Takeaway
VB6 event procedures are the foundation of interactive applications. Understanding how to structure code, handle events, and perform calculations is essential for creating responsive VB6 programs.
Welcome to Lesson 4 of our Visual Basic 6 Tutorial! In this lesson, you'll learn how to write effective VB6 program code to create interactive applications. We'll cover event procedures, control properties, calculations, and more with practical examples you can implement.
4.1 Introduction to Writing Code in Visual Basic
Each control or object in VB6 can initiate various events. These events are neatly cataloged in the dropdown menu within the code window. To unlock this menu, double-click on an object and pick your preferred event from the procedures' box.
1 Event Categories
Events cover form loading, command button clicks, keyboard key presses, object dragging, and more.
2 Event Procedures
For every event, you must compose an event procedure outlining the actions to be executed.
4.2 Accessing the Code Window
To start writing code for an event procedure, double-click an object to enter the VB code window. For example, if you want to write code for the event of clicking a command button, double-click the command button and enter the codes in the event procedure.
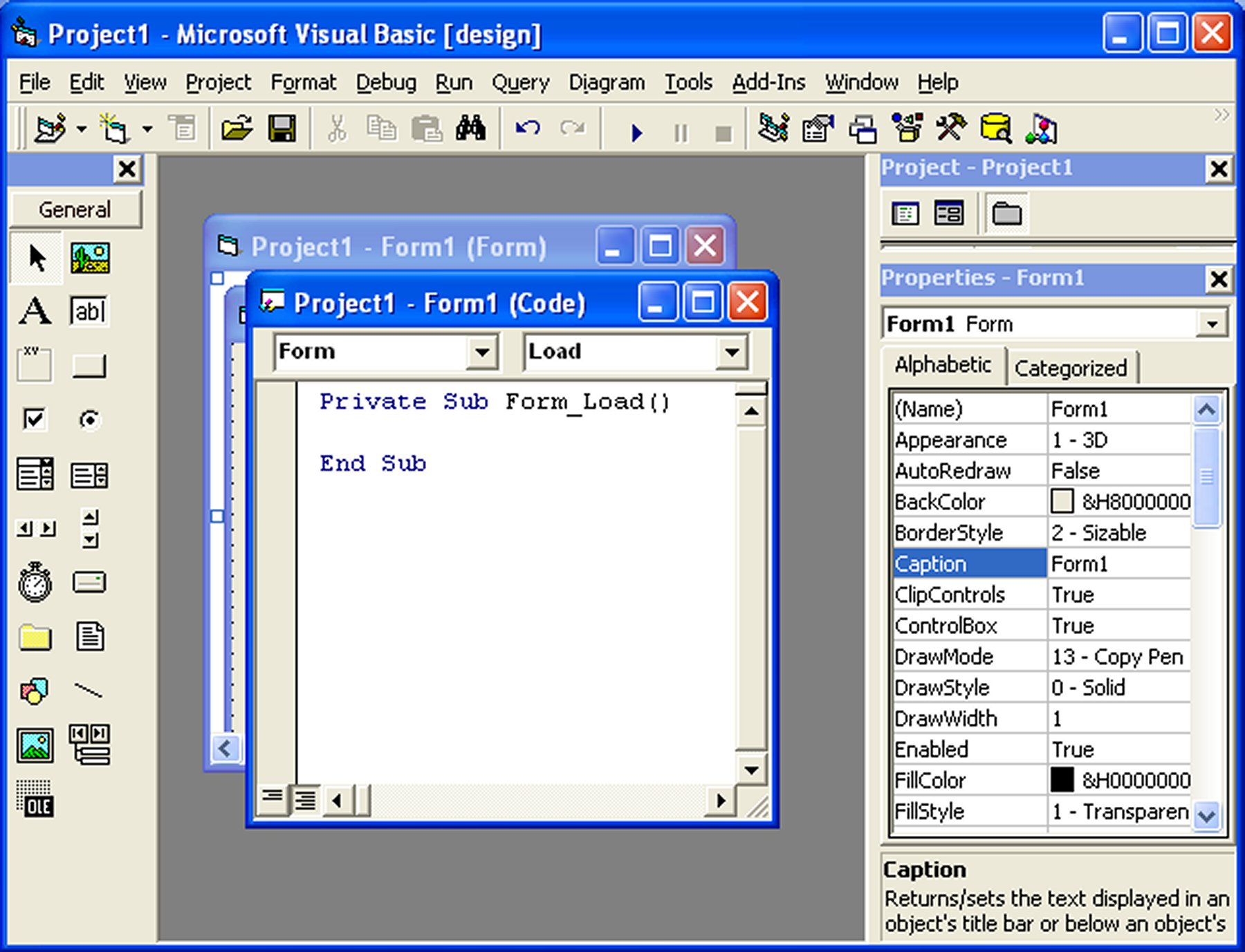
4.3 Structure of an Event Procedure
The structure of an event procedure follows this pattern:
Private Sub Command1_Click() ' VB Statements End Sub
4.4 Writing VB Statements
You enter the codes in the space between Private Sub Command1_Click and End Sub. The keyword Sub stands for a sub procedure that makes up part of all procedures in a program or module.
Important Syntax
The syntax of Visual Basic's program code resembles the English language, making it relatively easy to learn. Common keywords include Print, If...Then...Else, For...Next, Select Case, End, and Exit Sub.
4.5 Understanding Object Properties
The syntax to set the property of an object or to pass a certain value to it is:
Object.Property
Where Object and Property are separated by a period. For example:
Visibility Control
Label1.Visible = True
Makes Label1 visible
Text Assignment
Text1.Text = "Hello"
Sets textbox content
Component Control
Timer1.Enabled = False
Disables Timer1
4.6 Examples of Event Procedures
Example 4.1: Changing Label Visibility and Text
Private Sub Command1_Click() Label1.Visible = False Label2.Visible = True Text1.Text = "You are correct!" End Sub
Example 4.2: Updating a Label and Image
Private Sub Command1_Click() Label1.Caption = "Welcome" Image1.Visible = True End Sub
Example 4.3: Showing Picture Box and Starting Timer
Private Sub Command1_Click() Picture1.Visible = True Timer1.Enabled = True Label1.Caption = "Start Counting" End Sub
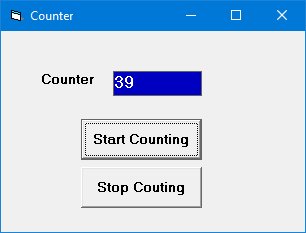
Example 4.4: Building a Counter
This counter starts counting after the user clicks the command button. We use a label as a counter, two command buttons, and a Timer control.
Timer Control Properties
The Timer's Interval property determines how frequently the timer changes. A value of 1000 represents 1 second. In this example, we set the interval to 100 (0.1 second). The Timer's Enabled property is set to false at design time so the program only starts counting after the user clicks the button.
Dim n As Integer Private Sub cmd_StartCount_Click() Timer1.Enabled = True End Sub Private Sub cmd_Stop_Click() Timer1.Enabled = False End Sub Private Sub cmd_Reset_Click() Lbl_Display.Caption = 0 n = 0 End Sub Private Sub Timer1_Timer() n = n + 1 Lbl_Display.Caption = n End Sub
Counter Simulation:
Click "Simulate Counter" to start
Example 4.5: Click and Double Click Events
This program displays a message indicating whether a label was clicked once or twice.
Private Sub MyLabel_Click() MyLabel.Caption = "You Click Me Once" End Sub Private Sub MyLabel_DblClick() MyLabel.Caption = "You Click Me Twice!" End Sub
Click Simulation:
Click the button to simulate single/double click

Performing Calculations in Visual Basic
Program code that involves calculations is fairly easy to write, similar to mathematics. However, you need to know the basic arithmetic operators in VB:
Multiplication
Use * instead of ×
Division
Use / instead of ÷
Exponentiation
Use x ^ n for xn
Square Root
Use Sqr(x) for √x
Critical Functions: Val and Str$
Two important functions for arithmetic operations are Val and Str$:
- Val converts text to a numerical value
- Str$ converts numerical to a string (text)
Failure to use Val will result in incorrect calculations when working with text inputs.
Example: Type Conversion with Val Function
Without Val Function
Private Sub Form_Activate() Text3.Text = Text1.Text + Text2.Text End Sub
With Val Function
Private Sub Form_Activate() Text3.Text = Val(Text1.Text) + Val(Text2.Text) End Sub
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've learned essential VB6 coding techniques:
Event Procedures
Mastered the structure and creation of event procedures for various controls
Object Properties
Learned to manipulate properties at runtime to create dynamic interfaces
Timer Control
Implemented a functional counter using the Timer control and event handling
Type Conversion
Understood the critical importance of Val and Str$ functions for calculations
You've now built interactive VB6 applications using proper coding techniques and are ready to explore data types in the next lesson.
Next Lesson
Continue your VB6 journey with Lesson 5: VB Data Types.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 6 Made Easy
The ultimate beginner-friendly guide for mastering Windows-based application development using Visual Basic 6. Used as a textbook by universities worldwide.
What You'll Learn:
- Comprehensive coverage of VB6 coding techniques
- Event-driven programming best practices
- Practical examples and projects
- Debugging and error handling
- Database integration
- Advanced UI development

Visual Basic 2022 Made Easy
The ultimate guide to VB.NET programming in Visual Studio 2022. Master modern VB development with this comprehensive resource.
What You'll Learn:
- Modern VB.NET coding techniques
- Visual Studio 2022 features
- Advanced UI development
- Database programming with ADO.NET
- Web API integration
- Deployment strategies